Leica M Monochrom Digital Rangefinder Camera - Page 22 Index of Thorsten Overgaard's user review pages on Leica M9, Leica M9-P, Leica M-E, Leica M9 Monochrom, Leica M10, Leica M10-P, Leica M10-D, Leica M10-R, Leica M10 Monohcrom, Leica M11, Leica M11-D, Leica M 240, Leica M-D 262, Leica M Monochrom 246, Leica SL, Leica SL2, Leica SL2-S, Leica SL3, Leica SL3-S as well as Leica TL2, Leica CL, Leica Q, Leica Q2, Leica Q2 Monochrom, Leica Q3 and Leica Q3 43:
Add to Flipboard Magazine.
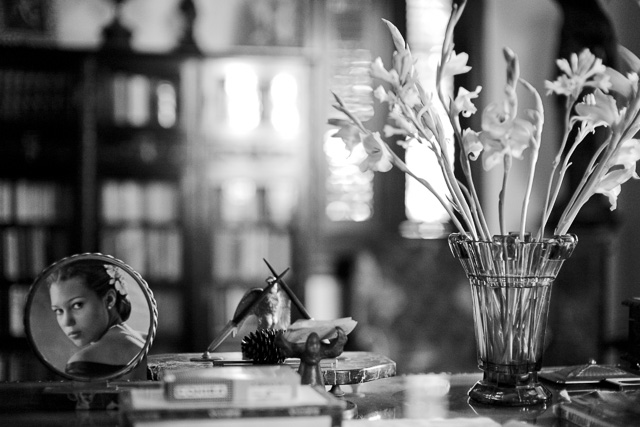
Writing light letters by the moonlight
By: Thorsten Overgaard. March 6, 2013. Latest edit April 24, 2020.
I woke up in the middle of the night some months ago and yelled, "I don't want to be a landscape photographer!" and then fell back asleep.
A nightmare, clearly.
I don't have any rules for what I don't want to photograph, nor have I warned my kids against becoming landscape photographers, and I probably have done a few pictures that would qualify as landscapes. But what people mostly point out to me is that there are people in most of my images, and rightly so.
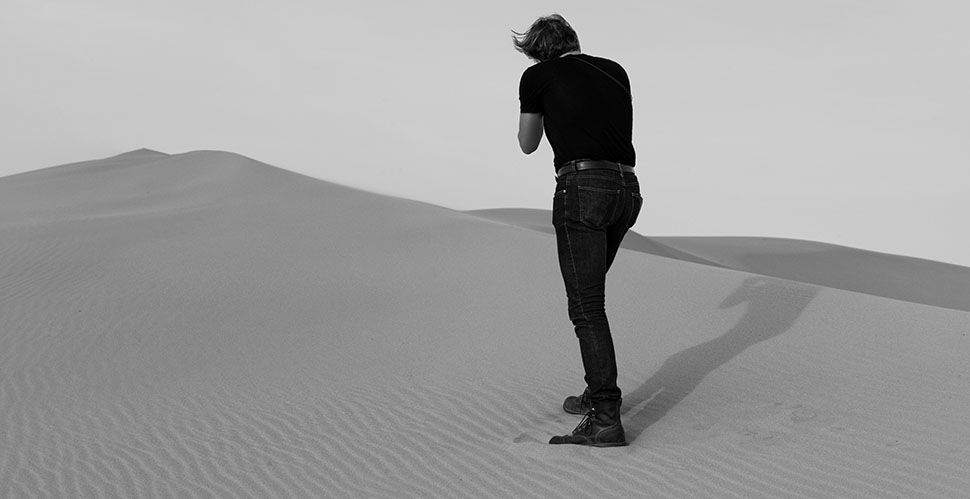

Thorsten Overgaard in Qatar by Khalid Al-Thani.
But maybe it was some irony of life that I recently found my self spending nine days shooting landscapes in Qatar. Whilst I did not find myself very succesful in making any landscape pictures I found interesting, I worked with Khalid Al-Thani whom I may tell more about later. He is rather discrete about his photography, and I would like to change that to a more public profile as he has a very intersting eye for landscape, light and patterns.

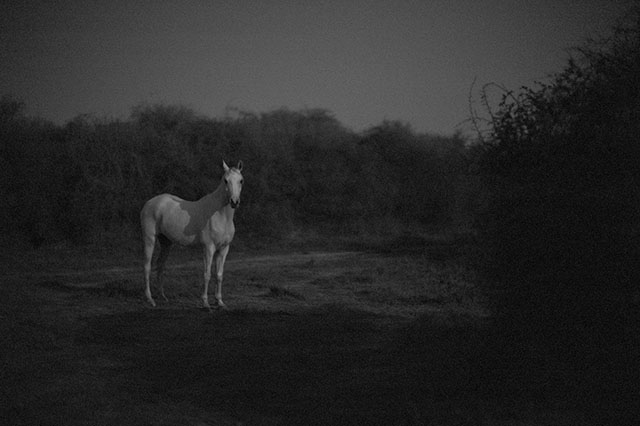
The White Horse in Doha, Qatar, January 2013. Photographed in the last minutes of the sunset light, Leica M Monochrom (2012) with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 (2008). Adjusted in Lightroom 3. 320 ISO, 1/4.000, f/0.95. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Working with someone else is always interesting because you get to understand what they see, and mainly to see what they saw when you didn't think there was anything to see. I've given the example many times, that if you take four photographers with the same camera and the same lens and have them photograph the same scene at the same time, you will get four very different views.
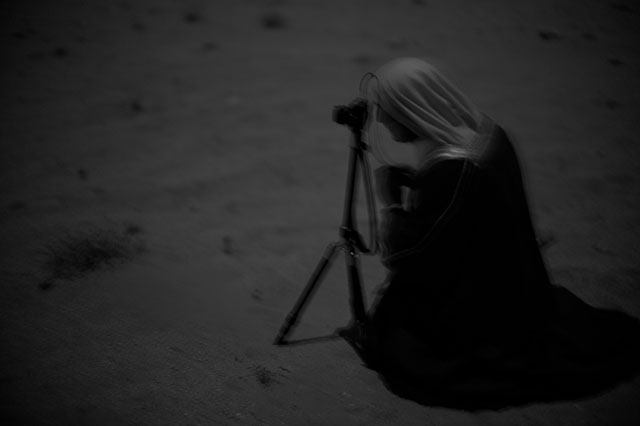

Khalid Al-Thani with his Leica in the moonlight of Qatar. © Thorsten Overgaard.
In my opinion - and experience - walking and working with other photographers is very interesting and can nothing but expand your own view and/or clarify for yourself how your own photography represents a unique viewpoint from others.

Khalid Al-Thani working with the Leica Visoflex 65mm Macro Elmar f/3.5 to get some details of the wings (the lens goes from macro to infinity). Leica M Monochrom (2012) with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 (2008). Adjusted in Lightroom 3. 320 ISO, 1/4.000, f/0.95 with B+W 3-stop ND-filter. © Thorsten Overgaard.
We all expect that what we can photograph, anybody else can photograph too. Not so. Far from the truth. Your viewpoint is very unique, and if you knew just how unique, you would appreciate your own photographs much more and envy others' less.

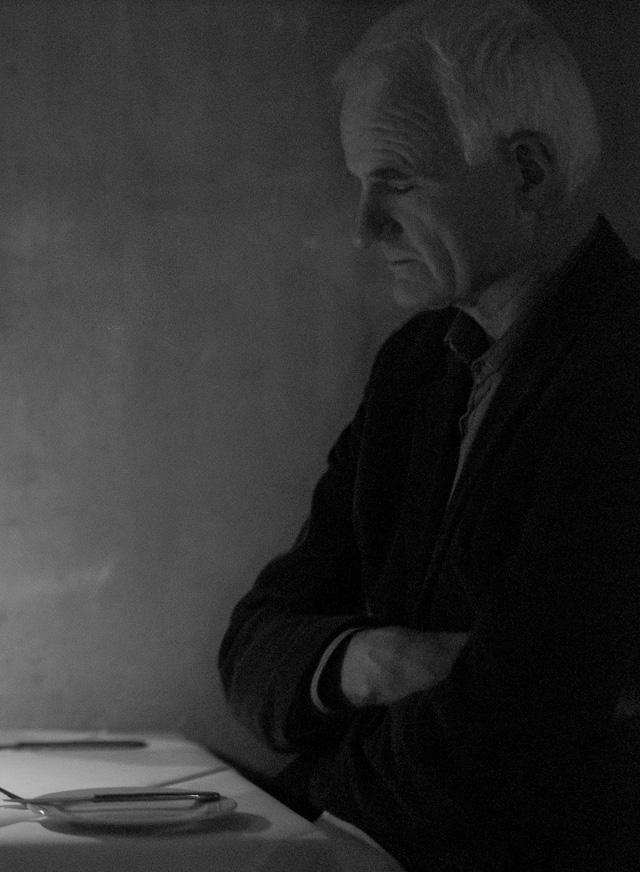
The bird man. Leica M Monochrom (2012) with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 (2008) with B+W 3-stop ND filter. 320 ISO, 1/2000 second. © Thorsten Overgaard
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Buy the new eBook
"Composition in Photography"
by Thorsten von Overgaard |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Composition in Photography
- The Photographer as Storyteller
This book will inspire your photographic eye and make you wonder about all the possibilities you can now see.
In this exciting new book Thorsten Overgaard expands and simplifies the subject of composition. It's elevated from geometric patterns to actual storytelling by practical use of space, rhythm, time, colors, emotions and intuition in your photography.
- The Basics of Composition.
-
Composition in the Third Dimension.
- Picture Stories.
- Accenturating with Light.
- Photograph as a Melody.
- Which lens are you?
- Fear of sharpness?.
- Vanishing Point.
- The most important
element of composition
- What is the unknown secret
why it is you mostly can't get
the Rule of Thirds to work?
- How does a camera see
differently than the eye?
- What does quantum physics and
photography have in common?
- What's the greatest adventure you can
set out on in photography these days?
- A Sense of Geometry.
Only $398.00.
Order now. Instant delivery.
864 pages. 550 Illustrations. |
|
"It’s your best work so far"
"I’m being gently led"
" I love this book!!!"

"The book is incredible"'
"It’s like therapy for the human spirit."
"Beautiful and inspiring"
"Full of practical advice
and shared experience"
'I love how hands-on and
laid back Thorsten's witting style is"
"Inspiring"
"Intense and thought-provoking" |
|
| |
 |
 |
|
100% satisfaction of money back. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Night photography (and other adventures)
with the Leica M Monochrom, Leica M9 and Leica MP in Qatar
The adventure we set forth to do was mainly shooting landscapes by moon light. Some times with birds, camels or horses.
Our day would usually start with preparations after lunch, and in the afternoon we would drive out to a location in the desert, arriving in time to shoot in the sunset light. And usually an hour later - around 7 PM - the moon would be in position to shoot scenery with the moon as the only light source.
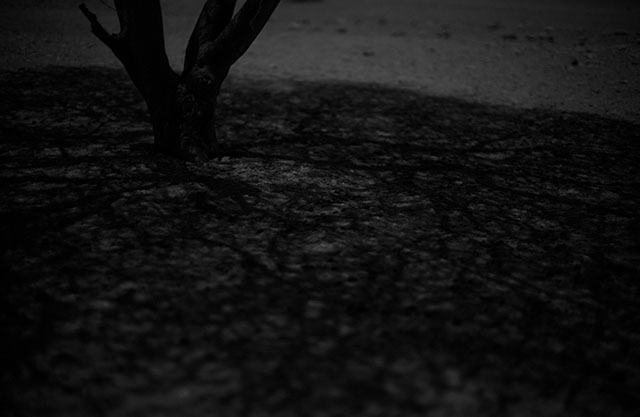

Shadows by moonlight. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 800 ISO, 1 second. Tripod. Finished in Lightroom 3. © Thorsten Overgaard.
I of course cheated a little by implementing people in my photographs, and by doing so I might have proven my own opinion about each photographer making each scenery fit his own viewpoint. Khalid would see patterns and light and follow his photographic goal of communicating the atmosphere of the Qatar desert. I would find people, light or other living things to communicate.

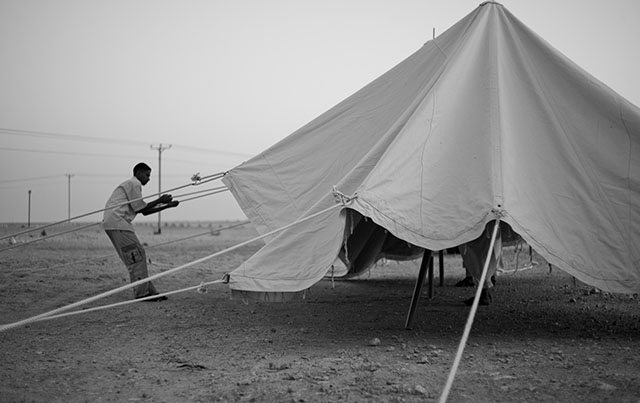
Brothers of the desert. Whilst we were setting up a rather complicated scenery with camels at sunset, a father and five of his sons (living in the desert) came by in their Land Rover. For me a chance to do portraits and candid photos of the sons. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 320 ISO, 1/1000 sec, f/0.95 with B+W 3-stop ND-filter. Finished in Lightroom 3. © Thorsten Overgaard.
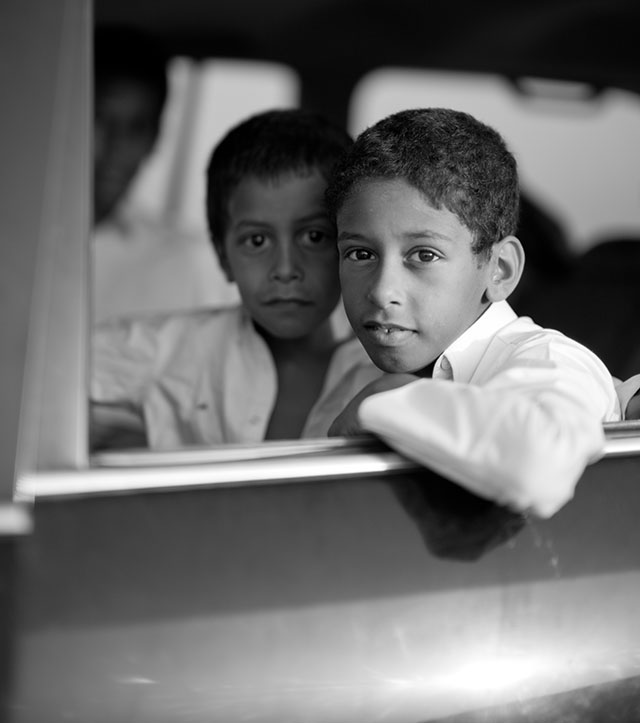

The two broters in their car. © Thorsten Overgaard.

But the conditions was not set by me. I was placed in a (for me) foreign landscape with challenging light conditions both at day and even more so at night. To play with composition and light where there were no light and not many elements to compose.
In other words, it was a challenge and a learning experience for both of us; working side by side with expressed and unexpressed preferences.

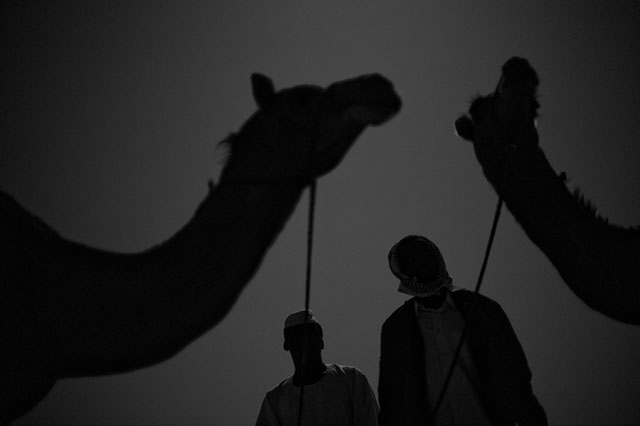
Khalid Al-Thani photographing a landscape with tripod by moonlight. We worked with double exposures and both Leica M9 (2009), Leica M Monochrom (2012) and Leica MP (2003) loaded with 400 ISO film. I did several of these similar looking, but decided for this one with some headlights from a car some miles away making the image more alive. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 (2008). 400 ISO, 4 seconds, tripod. Finished in Lightroom 3. © Thorsten Overgaard.
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
New eBook from Thorsten Overgaard:
"The Portrait Book
– How to Make People Look Beautiful" |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |

"Love the book.
Very insightful and very well done"
"You are my favorite author" |
|
Questions answered in this new eBook:
- What’s the secret behind Mona Lisa?
- How do you make anybody look beautiful?
- What is the right timing for portraits?
- What do you say to the people?
- How to photograph your spouse?
- How to edit portraits?
- What is the one right thing in all portraits?
- How to do research for portraits?
- What is the secret to light in portraits?
- Which lens to use for portraits?
- What is the composition rules for portraits?
- How to photograph children?
- Who should I photograph?
- How to do street portraits?
- and more...
Buy Now. Instant Delivery.
Only $298.00
578 pages.
Released April 5, 2020
|
|
| |
#1905-0119 |
|
100% satisfaction or money back. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
High ISO experience
One of the freedoms of the Leica M Monochrom (2012) that you soon start to appreciate is the ability to turn the ISO up to 3200 and 6400, and even 10000 if you must. With a lightstrong lens as the Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 or a Summilux f/1.4 there is hardly anything you can't photograph.
If you look at the images on this page you will see that very few are really high ISO. Because when you shoot in almost complete darkness, your chances of getting a good picture handheld at very high ISO are not that good.
I did a few handheld pictures but soon turned to tripod. One thing was that we were trying to emulate 400 ISO of the film cameras on most cameras, and for some images, we wanted motion blur and/or multiple exposure.
But the next concern was the quality of details.
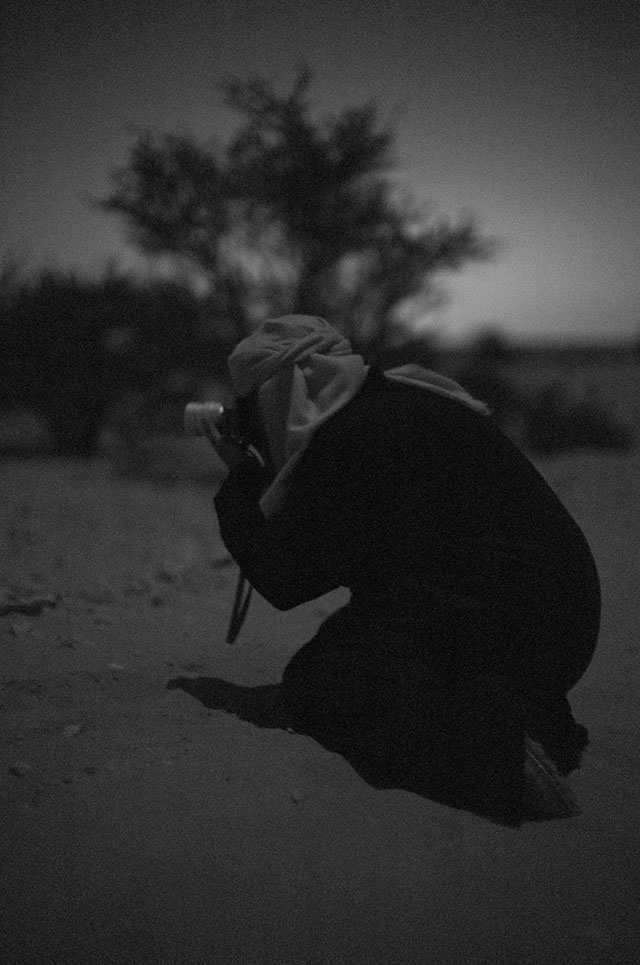

Khalid Al-Thani photographing by moonlight with the Leica M9 Hermes and the silver Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95, 10,000 ISO, 1/8 second. Edited in Lightroom 3. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Capturing details and aesthetics in low light
The point of it all was not so much having low light, but to have a different type of light. I will later be finishing an interview with lens designer Peter Karbe about the Leica 50mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH that he was the lead designer of (as he was on the Leica 50mm Summilux-M ASPH f/1.4, the 35mm Summilux-M ASPH f/1.4 FLE (FLoating Element) and the 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95).
One of the things he told me a couple of weeks before was ringing in the back of my head as I stood in the dark and cold desert, freezing by the camera on the tripod.
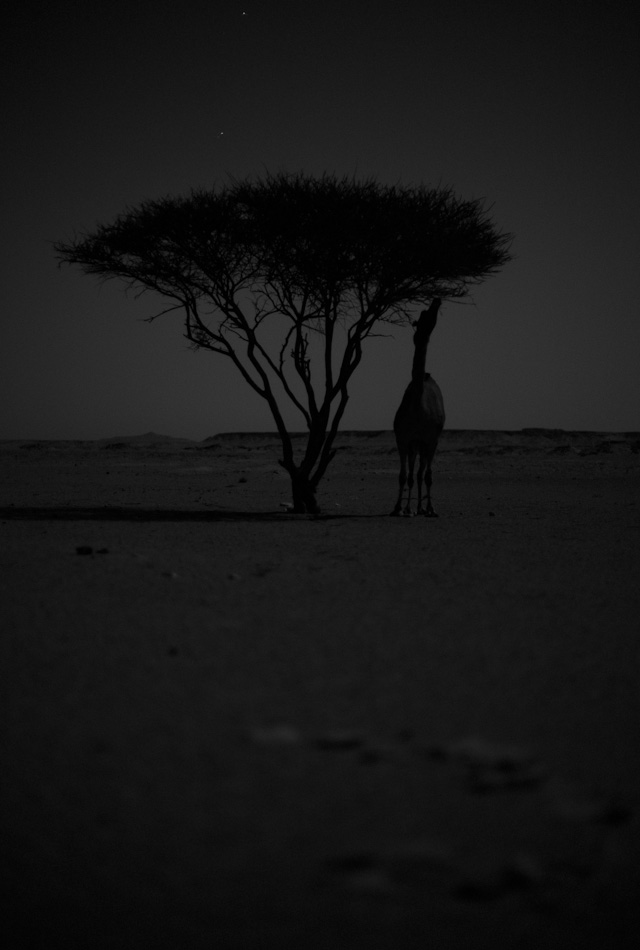

Camel by tree in moonlight. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 1600 ISO, 1/8 second. Finsihed in Lightroom 3. © Thorsten Overgaard.
On a final note about how to perfect the lens design further, he said, "it's easy to take photos when there is light. It's another thing to take photos when there is no light."
He wasn't referring to my upcoming desert experience but to the fact that Leica lenses such as the current 35mm and 50mm Summilux and the 50mm Noctilux, as well as the new 50mm APO-Summicron seem to see more shadow details than the human eye.
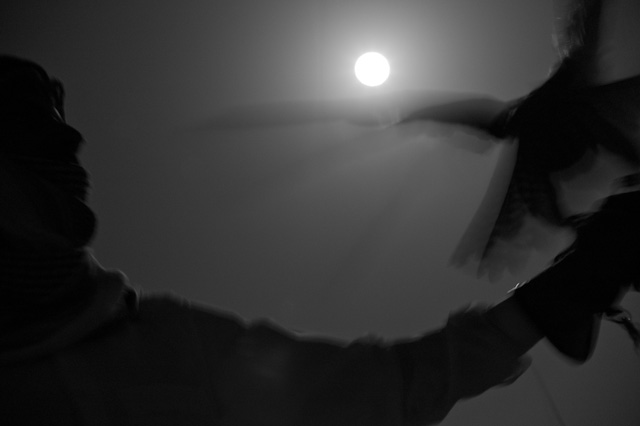

Photographing birds by moon light. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 1600 ISO, 1/4 second. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Now, he see lens design and the light in a few more dimensions than just what is captured. He has some ideas about how the quality of it should be, both what is in focus and what is out of focus. All very interesting, and in the coming months or years I will try to translate his vision into pictures and articles. More on that, later.
But how should a landscape, patterns, surfaces and all look in an image, when what the human eye can see is quite limited? That was one of the things I spent some thoughts about both in the desert where the preview would light up on the cameras display as strong as a cars headlights. And then again when I had the images on the computer.

The camp at night. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH F/0.95. ISO 400, 3 seconds. © Thorsten Overgaard.
You can correct the exposure and all a great deal, but how should an image taken in darkness look? At some point it looks like daylight or sunset when it was in reality pitch black. On the other hand, a pitch black photo wouldn't communicate anything. So where is the balance between pitch black and a level where you can see the details, the surfaces and it contain some form of aesthetics?
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Buy the new eBook
"A Little Book on Photography"
by Thorsten von Overgaard |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |

Order now - Instant delivery.
More info
★
★
★
★
★
★ |
|
It's a humorous understatement to call this
new eBook by Thorsten Overgaard for
"A Little Book on Photography".
It's a grand book, a history lesson, life experience, a biography and poetry book and brilliant photo book!
All in one beautiful package of 180 pages
to fire you up and get you to love
photography ... unconditionally!
"A Little Book on Photography"
eBook for computer, Kindle and iPad.
New release March 2017.
Intro price only $47 - 180 pages.
| |
|
|
| |
Buy Now

Instant Delivery |
|
| |
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|
A new way of painting with light
The word photography comes from "painting (or writing) with light" and is of course in many ways in family with the work that painters used to do before we became able to record light with chemistry on glass plates (and later on plastic and now recorded digitally).
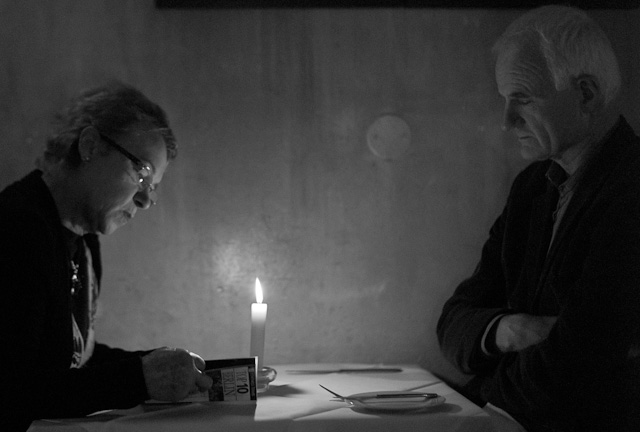

Berlin, Leica M Monochrom (2012) at 3200 ISO with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M f/1.0, 1/350 sec
I remember my surprise when I did some photos in Berlin back in October 2012 in a restaurant in Berlin. I shot at 3200 ISO at 1/350 of a second.
Where high ISO images often can look like daylight with a plastic and unnatural look to them (because it's not daylight but low light boosted to an unnatural level), these Leica M Monochrom pictures looked different.
In a way closer to reality, but at the same time with something added that is partly the actual low light (a candle light), partly the way the sensor and lens work.

Berlin. Leica M Monochrom at 3200 ISO with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M f/1.0
This was done with the old designed Leica 50mm Noctilux-M f/1.0, and one of the qualities of the new Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 is that it captures details in the darkness better.
In daylight the old and the new Noctilux have much in common, only the new is a bit more contrasty and a bit sharper.
But in darkness the difference should be even more visible.

The White Horse by moonlight, Qatar. Leica M Monochrom
with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 6400 ISO, 1/12 second. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Defining a unique style
A lot in photography has to do with finding out what ones own style is, and either as part as that, or as the next step, to move it to an even more individual style. Like a painter back in the day would start by learning the technique, then see what the great masters did, and then eventually develop his own technical skills and style, along perhaps with a different way of showing things (as for example Picasso did).
In photography we can distinguish our style by the choice of sensor (or film type, brand and developing technique), by the choice of presentaion and print (as in paper types and/or developing skills and techniques in a darkroom), and by finding lenses that few others use.
One way of making it special and unique. This painful slow video (yet interesting) show Platinum Palladium Printing with Leica M M
Photogravure
Also read the article by Max Marinucci about photogravure (a modern variant of the classic copper-plate photogravure process) of images from the Leica M Monochrom. He did a spendid article on Steve Huff called "The Future Is In The Past – The Leica Monochrom and Photogravure" about it.
There's plenty of ways to develop a distinct style, either by accident or by exploring. But you get the picture.
And the Leica M Monochrom opens up for some obvious possibilities because it behave differently, and because it is a new and unexplored camera type.
What is interesting here is not the cameras ability to go high in ISO, but how the sensor and lens together paint the light when there is no light.
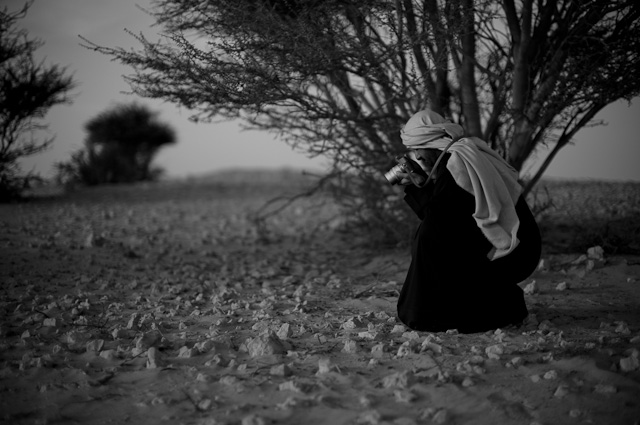

Khalid Al-Thani in one of his tiredless attempts to find and capture patterns and light for which he has a very good eye. Leica M9 with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. © Thorsten Overgaard.
The third element of course is how you light the scenery. Moonlight, candlelight, headlights of a car, winter darkness ...
But it is evident that where quality light is usually defined by the size of the light source (and not the strength), shooting with no light is not actually no light if the exposure is long enough; but a type of light with qualities you cannot necessarily judge by the eye.
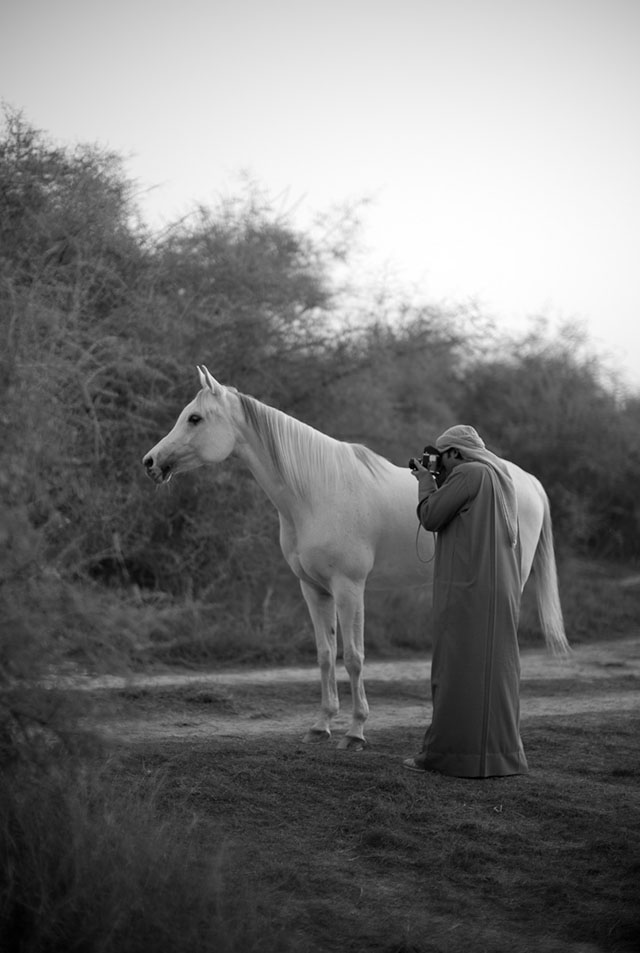

Khalid Al-Thani working with the Leica Visoflex 65mm Macro Elmar f/3.5 to get some details of the horse (the lens goes from macro to infinity). © 2013 Thorsten Overgaard. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95 with B+W 3-stop ND-filter. 320 ISO, 1/750 second. Finished in Lightroom 3. © Thorsten Overgaard.
 |
NEW VERSION 11.3 |
 |
| |
 |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Buy Now. Instant delivery.
New Version 11.3
ONLY $698.00

Now includes
4+ hours of
video tutorials.
100% satisfaction
or 100% refund.
More info.
|
|
| |
#2130-1121-3 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Update to Version 11.3
Apply
code "UPDATE113" on checkout to get this complete version 11.3 update.
$298.00

Updates all previous Surival Kit versions since 2009. |
|
| |
|
|
Buy the complete new
Lightroom Survival Kit 11.3
The Legendary Tutorial for Photographers
Brand-new JUNE 2022-version.
Now with brand-new 4+ hours of video tutorials.
New sections on compostition and storytelling.
How to edit color photos.
How to edit black & white photos.
How to do keywords logical and easy.
The most successful photo editing kit ever
Photographer Thorsten Overgaard first released the Lightroom Survival Kit in 2009 and have honed it with new and fresh updates. This Version 11 is the most radical updated and renewed version ever, four years in the making.

Professional workflow experience made simple, logical and easy to use.
Master editor makes it simple to understand
The Survival Kit is unique and one-of-a-kind being made for photographers for photographers. When someone understands their subject, they can explain it so it is easy to understand. The hallmark of Thorsten Overgaard is to make expert knowledge shown and told in a way so anyone can apply it.
Hands-on advice that works
With a 450 pages workbook and 4+ hours of video, every element of digital photography is touched on, in handy chapters and pre-flight checklists. Editing of color vs black and white photos, keywording, cropping of images, fine-tuning of tones, color balance and color control, export of originals, printing, archiving and backup, and much more.
Comes with the Overgaard Leica Presets (Value $48)
The Lightroom Survival Kit comes with Thorsten Overgaard's special-made Lightroom Presets for all digital cameras and for Leica digital cameras.
Understand all from camera to the final print
Chapters in this version goes over the background for High Dynamic Range (HDR), digital raw files and how to set up a professional photography workflow, from calibrating the screen to editing in Lightroom, and to making a final print. And more ...
10+ years experience in one package
No need to spend years figuring out the smartest way to do things when you can tap into the best way of doing things right here. The workflow of Thorsten Overgaard as been refined through years of field work with more than a thousand workshop attendees.
This method of workflow now used by thousands
The Survival Kit has been taught to thousands in workshops and in this Survival Kit. What does it do? It make you enjoy taking and making photos, and it increases your production considerabely. Most important of all, it'll give you back ownership of your files (which you will understand why is so important, once you have bought the Survival Kit and started applying its methods).
| |
|
|
| |
"Thorsten's methodology is perhaps not what hardware-, software- and cloud-companies want us to do, but as a former IT engineer I can only acknowledge his views about preserving our digital heritage. This workflow explained is for me the best I have ever seen".
★★★★★ |
|
| |
|
|
Video tutorials, image files, presets, checklists, definitions, tutorials of Lightroom, that boils down years of experience to a workflow you can implement in less than one day.
Start working in minutes. |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
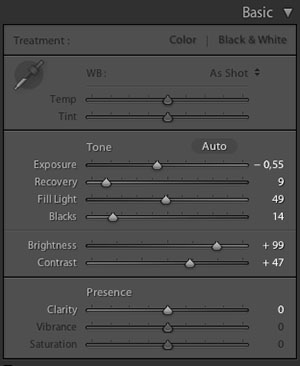
Editing in Lightroom 3 or Lightroom 4
I have never found Lightroom 4 amazing, which is why I still use Lightroom 3 (as of March 2013). My basic viewpoint is that I find the tones in LR4 unreal, and I suspect that the extreme controls of tones added in LR4 is what makes it look fake. It looks like a digital rendering (which it is; but a bad one).
One can use LR4 in classic mode, meaning one can still edit as if it was LR3 controls, or (as I have done so far) continue to use LR 3.6. I keep an install of LR 3.6 on my harddrive for students in my workshops, and you can download it here. It works as any other Lightroom installation with a 30 day trial, and then you have to insert the serial number you got with your Leica camera (and I shouldn't mention that if you change your computer's date forward a couple of years when installing and opening for the first time, then change it back to present time, you will add a couple of years to the trial period. But I do some times mention that little wellknown fact to people who want to try it for longer. But do buy and pay for software if you use it frequently and/or when you feel able to pay for it).
The reason it doesn't matter much if you use LR3 or LR4 is that the actual 'engine' to convert your RAW files is the Camera Raw in any case, and that is the same. It is a separate download and update on your computer (that happens automatically with the Software Update on your Mac).

Camels by moonlight. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 3200 ISO, 1/2 second. © Thorsten Overgaard.
| |
 |
| |
Lightroom 3 sliders in the Basic Editing Tool goes from 0-100 where the sliders in LR4 goes from -100 to +100 |
| |
|
Process Version 2010 vs. Process Version 2012
When importing images into Lightroom 4, you use PV 2012 (Process Version 2012), whereas Lightroom 3 uses PV 2010. You can select when importing which version you wish to use, hence which Basic Editing Tools you get. The Lightroom 4 offers extreme tonal editing, LR 3 a more 'natural' tonal editing - in my opinion.
This is based on Leica M9 and Leica M Monochrom and the way I work.
However, the reason given by Adobe to upgrade is that new camera-sensors of today offer more data to work with, hence the sliders should offer more (extreme) possibilities to use that extra space. But also they wanted to make the sliders more logical, as well as adjustments in JPG and RAW files compatible.
What does matter is how the software uses the Camera Raw, and LR 4 simply allows you to go more extreme on adjusting the image. And in my opinion, too extreme and/or in a not very classic aesthetic way. This might change with future sensors, such as the Leica M Type 240 or others, so don't get locked in LR 3 forever.

Setting up camp. Leica M9 with Leica 50mm Summicron-M f/2.0 II (1956). © Thorsten Overgaard.
The blind leading the blind
Look at the picture and find your own style of editing and tones you are satisfied with. The more I read about Adobe Lightroom and the update, the more I am convinced that they tend to look at how to adjust histograms (even tones all over the field by lessening highlights and softening up shadows), rather than actually making skin tones look like skin tones, or a Greek pillar look like a Greek pillar.
And LR 3 is still faster than LR 4, and only recent 2020-updates of the Lightroom Classic CC have picked yp the speed of the "good old" Lightroom 3.
Speaking of LR4, I should repeat my warning about LR4 - and most software for that matter - that when you update LR3 to LR4, the software will suggest you update all your image files "as it might improve" them. It might improve noise and other things, but it also changes the exposure and all other adjustments. Hence, if you just update all your files, the edits you did so far will not look as you edited them. Bad idea, really. I want to kick someone when I see software companies suggest so ruthlessly to follow their ideas. Adobe does state in blogs and elsewhere that one should apply updates individually, but they also built in a dialog box where you with one click can update all your files.
And that goes for any other use of software on computers, firmware update to cameras, etc. Do a little research first and be sure you have a way back, or at least don't enter a one-way street with no way back before you know where it is going. I don't have to mention Apple Maps to make the point clear.
Finally, to make it really clear: LR 4 is not a prerequisit for editing Leica M Monochrom or Leica M Type 240 files.

Camels in the moonlight. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. 1600 ISO at 1/6 second. © Thorsten Overgaard.
The final image is the final image
Your images should not be subject to continuous update. You saw them, you took them and made a decision at that point as to how they should look. Leave them like that. That's how the world looked when you took them.
Updating the Camera Raw to latest camers
The updating happens automatically. And ... not that it has much to do with this article about the Leica M Monochrom, but yo may wonder anyways. The Camera Raw profile for Leica M Type 240. It's not out yet, but there is a beta test version here you can download and install till the automatic update happens of the final one: Camera Raw 7.4 Beta

On our way home to the base to import and edit images after a long day. We shot somewhat 4,000 - 5,000 images each during 9 days. 110 GB of images for my part. Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95
What's in your bag, Thorsten Overgaard?
Here's a couple of videos showing what I packed for Qatar, very similar to what I pack in my bags for travel, a days shooting, walking around and such.
In the day to day one should always wear a camera, and unless you have assignments or special things you need to photograph, the travel kit for a Leica M photographer can very well be just a camera and one lens over the shoulder, and then an extra battery and SD-card in the pocket. Stylish, always ready, and never a tired shoulder or painful back from carrying a camera.
Enjoy!
What's in Your Louis Vuitton "iCare" Camera Bag, Thorsten Overgaard from Thorsten Overgaard at Vimeo. Here I am packing a bag for a day in the desert where we drive from location to location.
What's in Your Louis Vuitton "Binocular" Camera Bag, Thorsten Overgaard from Thorsten Overgaard at Vimeo. Here I am packing my small bag for walking around a whole day.
The inside of a bag tells the real quality
The way I shop for bags is that I look for what's inside. The hallmark of a quality bag is that the inside is as high quality as the outside. Examplified in a Fendi bag I saw with calf skin outside, crocodile inside. It was a female bag, but a bag is in my opinion a personal gadget, and the inside of it should fill you with as much pleasure as the outside.
More nice stuff for the camera
For more bags, straps and all the extra stuff, visit the Page 7 of the Leica M9 article, "Sexy Stuff for the Worlds Most Sexy Camera"

Leica M Monochrom with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M f/0.95. 1600 ISO at 1/3 second. © 2013 Thorsten Overgaard
Leica Definitions
By Thorsten Overgaard. For full list of definitons, visit Leica Definitions
| |
 |
| |
1:2/50 the description says. But what does it mean? |
| |
|
1:
Basically means 1 divided with. But why is it on the front of the lens? If you look close, a lens will often say 1:2/50mm on the front, meaning it is a 50mm lens with an f/2.0 apterture. The 1: itself is a ratio, that indicates that the aperture diameter (25mm) is the ratio of 50mm divided with 2.
It's a strange way of writing product information on modern products, but here's how it's right:
a) A lens is called a 50mm lens because there is 50mm from the sensor to the center of focus inside the lens.
b) A lens is f/2.0 when the widest opening is 50mm divided with 2 = The lens opening is 25mm in diameter at it's widest. Had it been an f/2.8 lens (1:2.8/50), the widest aperture opening would be 50mm divided with 2.8 = 17.8mm.
35mm
a) 35mm lens is a lens that has a viewing angle of view is 63°vertically, 54° horizontally and 38° vertically within a 35mm film frame:
b) 35mm film format is a standard film format where the actual widt of the film is 35mm. In photography the frame within the widt of the film is 24mm (on the width) and 36mm (on the lenght of the film roll). 35mm was first used in 1892 by William Dickson and Thomas Edison for moving pictures with frames of 24 x 18mm, using film stock supplied by George Eastman (Kodak), and became the international standard for motion picture negative film in 1909 [later other formats came about such as Academy Ratio (22 x 16 mm), Widescreen (21.95 x 18.6 mm), Super 35 (24.89 x 18.66 mm) and Techiscope (22 x 9.47 mm)].
Oskar Barnack built his prototype Ur-Leica in 1913 as a device to test film stock and/or motion picture lenses and had it patented, but Ernst Leitz did not decide to produce it before 1924.
c) 35mm is often given as a comparison when talking about lenses in small cameras or cameras with other sensor/film format than the 24 x 36mm frame. The camera has a smaller sensor and hence uses a wider lens to capture the same image as a "35mm camera" would. Example: A camera with a 12 x 18 mm sensor has a 14mm lens on it, and even the lens is actually a 14mm, it is specified as a 28mm lens (35mm) which means that the resulting image is equivalent to a 28mm lens on a 35mm camera.
| |
 |
| |
The Leica 50mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH f/2.0 lens of 2012. |
| |
|
50mm
a) 50mm lens is a lens that has a viewing angle of view is 47° vertically, 40° horizontally and 27° vertically within a 35mm film frame.
b) 50mm lens is often compared to the human eye. Not because of viewing angle but because of size ratio. The 50mm lens is the lens that comes closest to the size that the human eye see things (whereas the human eye has a much wider angle of view [120-200°] than the 50mm lens [47°], thought a more narrow focus (your eyes may observe very wide but your focus is on a limited view within that angle of view).
AF = Auto Focus. The idea is that the camera does the focusing itself (the word auto comes from Greek "self").
APO = stands for "apochromatically corrected". In most lenses, optical design concentrates the focus of blue light and green light into a single plane, but red light falls slightly into another plane of focus. Red subjects, therefore, would be ever so slightly out of focus compared to blue and green subjects in the same frame. Not sure you'd ever notice though, the difference is so slight. This is the same basic principle that requires you to shift the focus for infrared photography, related to the wave length of red light. In APO lenses, the design and expense has been put in to making red light focus on the same plane as blue and green. Under a microscope you would see that all light subject is now in focus, creating a sharper image overall. Many manufacturers offer APO designs, but in most of these only the very center of the lens is APO corrected. Leica prides itself on making most of the frame APO correct.
If one look at the images produced by the APO lenses (Leica 90mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH f/2.0, the Leica 50mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH, and the Leica 50mm Summilux-M ASPH f/1.4 that is in fact APO-corrected), one will notice that the colors are really bright and alive, almost more real than to the eye.
Apochromat; ORIGIN early 20th century, made of the two words;
apo: Greek origin, away from
chromatic (Latin origin, meaing relating to color.
Aperture = The f/ stop on the camera that regulates how much light passes through the lens. On a f/1.7 lens the lens is fully open" at f/1.7. At f/2.0 the aperture inside the lens make the hole through the lens smaller so only half the amount of light at f/1.7 passes through. For each f/-stop (4.0 - 5.6 - 8.0 - 11 - 16) you halve the light. The aperture of the lens is basically the focal length divided with the f/-stop = size of the hole (28mm divided with f/1.7 = the hole is 45 mm).
ORIGIN: Late Middle English : from Latin apertura, from apert- ‘opened,’ from aperire ‘to open’.
 The aperture blades inside the lens is clearly visible in this photo by Eolake Stobblehouse. The aperture blades inside the lens is clearly visible in this photo by Eolake Stobblehouse.
| |
 |
| |
The camera in Aperture Priority Mode |
| |
|
Aperture Priority Mode. When the shutter speed dial on top of a Leica camera is set to A, it is short for “Aperture Priority” and allows the user to set a specific aperture value (f-number) while the camera selects a shutter speed to match it that will result in proper exposure based on the lighting conditions as measured by the camera's light meter. In other words, you set the aperture as priority (f/1.4 for example), and the camera calculates a shutter speed (1/250 of a second) that matches that. If you change the aperture to f/2.0 by changing the aperture ring on the lens, the camera will re-calculate the speed to 1/125 so as to get the same amount of light to hit the sensor (f/2.0 is half the light through the lens as f/1.4 and 1/125 if twice the amount of light on the sensor as 1/250).
| |
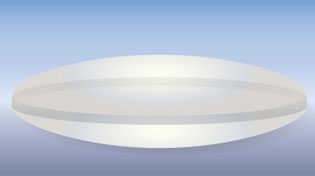
spherical (ball) |
| |

a-spherical (non-ball) |
| |
|
ASPH = (Aspherical lens) stands for "aspheric design".
Most lenses have a spherical design - that is, the radius
of curvature is constant. These are easy to manufacture by
grinding while "spinning" the glass. This design
however restricts the number of optical corrections that can
be made to the design to render the most realistic image possible.
ASPH lenses (a-spherical, meaning non-spherical), however, involve usually 1 element that does
*not* have a constant radius of curvature. These elements
can be made by 1) expensive manual grinding, 2) molded plastic,
or 3) Leica's patented "press" process, where the element
is pressed into an aspherical ("non-spherical")
shape. This design allows Leica to introduce corrections
into compact lens designs that weren't possible before. Practically,
the lens performs "better" (up to interpretation)
due to increased correction of the image, in a package not
significantly bigger than the spherical version.
There is another Aspherical lens manufacture technique: an uneven coating layer is applied to a spherical lens. The coating is thicker on the edges (or on the center, depending). Canon "Lens Work II" calls these "simulated" aspherical lenses. Simulated and Glass-Molded (GMo) asphericals show up in non-L Canon lenses, while the L lenses have actual ground aspheric elements.
A- means non, or without. From Latin, ex.
Sphere: ORIGIN Middle English : from Old French espere, from late Latin sphera, earlier sphaera, from Greek sphaira "ball".
| |
|
|
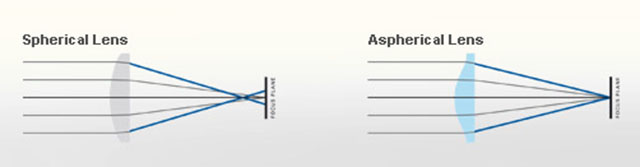 |
| Normal spheric lens (grinded) |
|
ASPH (note the shape of the glass as result of pressing rather than grinding) |
Auto- means “self”. The idea is that when a camera has auto-(something), it does that (something) by itself.
Banding = Noise in digital images. Horizontal lines in a horizontal picture (if the camera is in portrait mode/vertical, the lines will obviously be vertical). It's simply noise; the result of uncontrolled algorithms working overtime with an image the sensor really can't see because it's very dark. (If your image has vertical lines in it, it is more likely that the sensor needs remapping).

This image at 6400 ISO, underexposed and then brought up to correct exposure in Lightroom, displays banding: Horizontal lines in the image. Leica M-D 262 with Leica 50mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH f/2.0.
Base ISO = The ISO the digital sensor was born with. Even a digital sensor goes from say 50 ISO to 25,000 ISO, it only has one base ISO. Any other setting is an algorithm that figures out how the image whould look if there was 64 times more light, or half the light, etc.
When you go down from Base ISO (for example 200 to 100 ISO), you can expect a
decrease in quality. When you go up, the decrease is much less. For some sensors, you loose 2-3 stops by going down 1 step in ISO, but can go 8 steps up and only loose 1 stop in dynamic range. Basically, your ISO range should be from Base ISO and as far up as you can, before you see visible decrease in quality (mostly 3200 ISO - 6400 ISO).
Base ISO for Leica M9 is 160 ISO, for Leica M240 it is 200 ISO. For Leica M10 it is around 160 ISO. For Leica M Monochrom it is 320 ISO. For Leica Q and Leica Q2 it is around 100 ISO. For Panasonic Lumix S it is 200 ISO. For most Canon cameras the base ISO is around 100, for most Nikon cameras it is around 200 ISO.
Bokeh = The visual quality of the out-of-focus areas of a photographic image, especially as rendered by a particular lens: It's a matter of taste and usually photographers discuss a 'nice' or 'pleasant' bokeh (the out-of-focus area is always unsharp, which is why the quality discussed is if one likes the way it renders or not by a particular lens). The closer you get to something, the 'more' bokeh' you get (in that the focus becomes less for the background and foreground at close distances than at long distances). ORIGIN from Japanese 'bo-ke' which mean 'fuzzines' or 'blur.'.
 Bokeh: The visual quality of the out-of-focus areas of a photographic image. Photo at Bar del Fico in Rome. Leica TL2 with Leica 35mm Summilux-TL ASPH f/1.4. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard. Bokeh: The visual quality of the out-of-focus areas of a photographic image. Photo at Bar del Fico in Rome. Leica TL2 with Leica 35mm Summilux-TL ASPH f/1.4. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
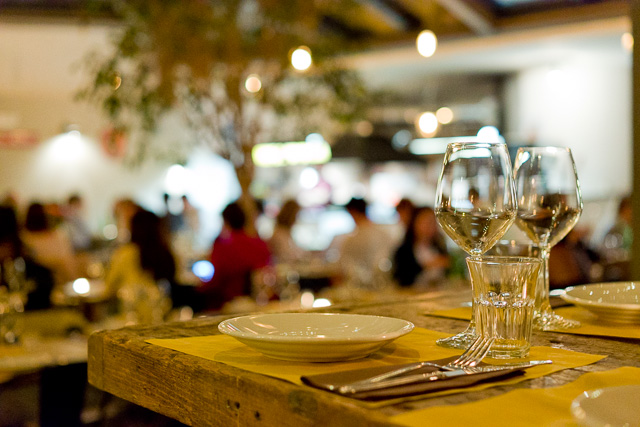
Burning = Expose one area of a photos more (in the development in the darkroom by exposing more light from the negative onto the light-senisitive paper by shading for all other areas than one with two hands forming a hole, or a piece of metal or paper with a hole in it). In modern digital post processing (using editing software liek Lightroom or Capture One Pro), a digital tool "burn" a selected area and makes it darker digitally. (Also see "Dodging").
| |

|
| |
C for continious |
C = Continuous shooting. When the ring by the Shutter Release on top of the camera (or in the menu of digital cameras that doesn't have such a feature on the outide of the camera) is moved from OFF to C, the camera takes series of images as long as the shutter release is pressed down. In some cameras the speed of continious shooting can be adjusted. For exampel in the Leica Q under the menu point Continuous Shooting you can define if the Continuous should be Low (3 fps), Medium (5 fps) or High (19 fps).
Camera - is today’s short name for Camera Obscura (meaning “a dark room”). Camera means Chambre and was used only as a Latin or alien word, actually only for Spanish soldiers’ rooms, until popularized in connection with photography in 1727: “Camera Obscura”. In 1793 the slang term “camera” was used by Sterne Tr. Shandy: “Will make drawings of you in the camera” and by Foster (1878), “The eye is a camera”. Camera Obscura was described by Iraqi scientist Ibn-al-Haytham in his book, “Book of Optics” (1021) and by Leonardo da Vinci in 1500; popularized and made widely known in 1589 by Baptista Porta when he mentioned the principle in his book “Natural Magic”. Johannes Kepler mentions Camera Obscura in 1604.
Camera = chambre (room), Obscura = dark (or cover).
| |
|
|
| |
Why is it called a "camera"..?
The word Camera is today's short name for Camera Obscura (which originally means “a dark room”).
Origin of the word Obscura means "dark" or "covered", and the word Camera means Chambre and was used originally only as a Latin or alien word, actually only for Spanish soldiers' rooms, until popularized in connection with photography in 1727: “Camera Obscura”.
In 1793 the slang term “camera” was used by Sterne Tr. Shandy: “Will make drawings of you in the camera” and by Foster (1878), “The eye is a camera”.

Ibn-al-Haytham mentioned Camera Obscura in his "Book of Optics" in 1021.
The concept of Camera Obscura was described by Iraqi scientist Ibn-al-Haytham in his book, “Book of Optics” (1021) and by Leonardo da Vinci in 1500; popularized and made widely known in 1589 by Baptista Porta when he mentioned the principle in his book “Natural Magic”. Johannes Kepler mentions Camera Obscura in 1604.
Camera = chambre (room), Obscura = dark (or cover). |
|
| |
|
|
CCD sensor (as used in Leica M8, M9, Leica S) = (Charged Coupling Devices) - The first digital cameras used CCD to turn images from analog light signals into digital pixels. They're made through a special manufacturing process that allows the conversion to take place in the chip without distortion. This creates high quality sensors that produce excellent images. But, because they require special manufacturing, they are more expensive than their newer CMOS counter parts.
CLA
An acronym for "(C)lean, (L)ubricate & (A)djust", whereby the item is merely re-lubricated, fine-adjusted and calibrated rather than repaired. "I just got my equipment back from CLA at Leica"
CMOS sensor (as used in Leica CL, Leica T/TL/TL2, Leica M 240, Leica M Monochrom Typ 246, Leica S Typ 007, Leica SL, Leica Q, Leica Q2, Leica M10, Leica X, Leica D-Lux, etc.) = (Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) chips use transistors at each pixel to move the charge through traditional wires. This offers flexibility because each pixel is treated individually. Traditional manufacturing processes are used to make CMOS. It's the same as creating microchips. Because they're easier to produce, CMOS sensors are cheaper than CCD sensors. CMOS allow Live View and use less energy than CCD.
Contrast - The degree of difference between tones in a picture. Latin contra- ‘against’ + stare ‘stand.’
Depth - Distance between front and back. Distance from viewer and object.
| |
 |
| |
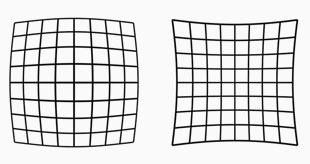
Lens distortion looks like this. The lines are not straight. Our eye uses distortion correction. Lens designers can design lenses so they have very little distortion, or they can make less complicated lens designs and "fix" the distortion in software. |
| |
|
Distortion = In photo optics/lenses: When straight lines in a scene don't remain straight because of optical aberration.
Lens designers can correct for distortion to a degree so the whole image field is perfect corrected and all lines remain straight. In modern lens design many designs rely on Software Distortion Correction (SDC).
The eye adjusts for distortion so we always see vertical and horizontal lines straight when we look at things. Even when you get new prescription glasses (if you use such), you will often experience distortion in your new glasses. After a few days they eyes have adjusted for the glasses and the distortion you saw to begin with is now gone. Software Distortion Correction (SDC) is far behind what the human eye can perform of adjustments. (Also see my definition on Perspective for more on the eye and optics)
DNG = Digital Negative, an open standard developed by Adobe. It is a single file that contains the raw image data from the sensor of the camera as well as date, time, GPS, focal length, settings, etc.
The alternative is a RAW file + XLM file where the RAW file contains the image information and the XML contains the rest of information about where, how and when the picture was taken.
A Camera Raw profile (that is specific for that camera) in the computer helps the software program, for example Adobe Lightroom, to translate the RAW data into the image.

A raw file (or DNG) is simply the full recording of digital data (1's and 0's) from the sensor. In the computer, the sensor data is translated into the exact colors, via a camera profile.
Dodging = Expose one area of a photos less (in the development in the darkroom by exposing less light from the negative onto the light-senisitive paper by shading for an area with a hand or piece of metal of paper). In modern digital post processing (using editing software liek Lightroom or Capture One Pro), a digital tool "dodge" a selected area and makes it lighter digitally. Also see "Burning")

Dodging in the darkroom using a piece of metal or paper to shade so a portion of the light-sensitive paper gets less light. Photo: richardpickup.
DOF = Depth of Field. This is how much of the image will be in focus or "acceptable sharp". The DOF is determined by the subject distance (the farther away, the larger area is sharp; the closer the focus is, the less of the lage is sharp), the lens aperture (the depth of field is narrow at f/1.4 and larger at f/5.6) and the focal length of the lens (tele lenses has very narrow depth of field whereas wide angle lenses has a wide depth of field) and film or sensor size (small-sensor cameras has a wide depth of field wheras medium format or large format cameras has a very narrow depth of field). As an example, a Leica 21mm Super-Angulon-M f/3.4 lens is sharp all over the focus field from 2 meter to infinity when set at a distance of 3 meters at f/3.4. The DOF scale measurement on top of the Leica lenses shows lines for each f-stop that indicates from which distance to which distance the image will be sharp. Shallow DOF is a generally used term in photography that refer to lenses with very narrow focus tolerance (which can be used to do selective focus; making irrelevant subjects in the foreground and background blurry so only the subjects of essence are in focus and catches the viewers eye).
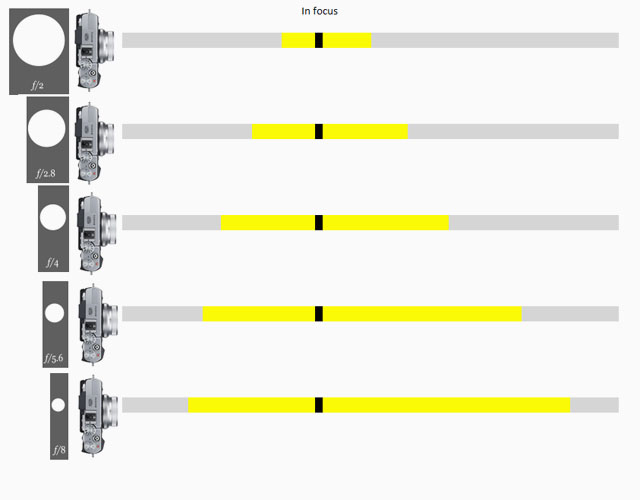
Depth Of Field scale from Fujifilm.

Depth of Field: Focus is on the flowers and the photograph on the desk and the foreground and background is blurred as the depth of field is narrow. If one stop down the aperture of the lens from f/1.4 to f/5.6, more will be in focus. If one stop down the lens to f/16 even more (if not all) will be in forcus. Another rule: The closer you go to a subject (the less focusing range), the more narrow the Depth of Field will be. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
DR = Dual Range lens. This is a type of Leitz/Leica lens that works as macro (near focus range) and normal lens, and comes with googles/"Eyes" for the macro function. The 50/2 Dual Range Summicron was made from 1956 to 1968, only in chrome, with a near-focusing range as close to 478mm.
You mount the googles/"Eyes" to focus at close range. If you use the lens in normal range, you can take off the googles/"Eyes"
The googles/"Eyes" can be critical for which camera the lens fits on. the Leica M6 TTL requires that the plastic tab onthe eyes is removed; and other Leica M models likewise. It fits on the Leica MP, M2, M3 and oterh models. .

Leica M2 with Dual Range Summicron-M f2.0. © Dave Dunne.
Dynamic range. The grade of ‘contrast range’ (or number of tones) a film or sensor, or simply a photograph, possess between bright and dark tones. The human eye is said to have a dynamic range of 10-14 ‘stops’ (but because we scan area by area and compile a concept of the overall scene, they eye is often thought to have a much higher dynamic range), Film used to have 7-13 ‘stops’ and some modern sensors have up to 15-17 ‘stops’.
ELCAN - Ernst Leitz Canada, established 1952, was the Leitz family's guarantee against another war in Europe and/or invasion from Russia after WWII. Besides becoming a copy of the Wetzlar factory, it also became the somewhat military/industrial branch of Ernst Leitz . Because of the precision work, high standards and knowledge in optics for science and millietary, the ELCAN plant was sold to Raytheon (USA), who bought it from its previous owner, Hughes Aircraft Co.

Ernst Leitz Canada (ELCAN) was established in 1952 close to Toronto in Canada.
Elcan-M is the name of lenses for M lenses that fits the Leica M system Leica M, as the U.S. Navy High Resolution Small Format Camera System during the Vietnam war.
Elcan-R is also the name of a series of R lenses made in the 1960ies and early 1970ies that fits Leica R system, as the U.S. Navy High Resolution Small Format Camera System during the Vietnam war.

The Leitz ELCAN-M 90mm Noctilux-M f/1.0 model C164 on a Leica KE-7 film camera made for the U.S. Navy.
Elmar = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f3.5 . Historically derived from the original 1925 50mm f3.5 Elmax lens, which was an acronym of (E)rnst (L)ieca and Professor (Max) Berek, designer of the original lenses. Later that year the 50mm f3.5 Elmar superceded the Elmax, which was discontinued due to its complexity and high cost of manufacture.
Elmarit = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f2.8 . The name is obviously derived from the earlier (and slower) "Elmar" designation. Not every f/2.8 lens is called an "Elmarit" though, the most obvious current exception being the 50mm f2.8 Elmar-M collapsible lens which for nostalgia and marketing reasons has kept the original 1930's Elmar name (the 50mm f3.5 collapsible Elmar, manufactured 1930-59, was one of Leica's most famous and popular lenses). Vario-Elmarit (and Vario-Summicron, etc) is Leica Camera AG's name for zoom lenses.
Elmax
Elmax lens named after = Ernst Leitz + Max Berak. Ernst Leitz was the founder of Ernst Leitz Optical Industry which later became Leica. Professor Dr. Max Berak was employed at Leica in 1912 and was the architech of the first Leica lens which Ernst Leitz asked him to design for the "Barnack's camera" (the 1913-prototype named after Oscar Barnack who invented it). The lens was a f/3.5 50mm and was known as the Leitz Anstigmat and later the Elmax.

The Leitz Elmax 50mm f/3,5 (1925-1961) on the Leica A camera (1925) camera. Photo by Marco Cavina.
Exposure Bracketing = The possibility to set the camera to automatically record a series of images where the exposure is above and below what the camera measures. The idea is that at least one of the images will be correctly exposed.
f/ (f-stop, also known as aperture).
f- (focal length). Often given in mm, for example 90mm. In the past they were often given in cm or inch, for example 9.5 cm or 3.2 inch.
f/1.25 is the size of the "hole through" the lens, the aperture. f/1.25 means focal length divided with 1.25. In the Leica 75mm NoctiluxM ASPH f/1.25, the "hole through" the lens at f/1.25 is 60mm in diameter. At f/1.4 the "the hole through" is 53.5mm in diameter. At f/4 the "hole through" is 18.75mm in diameter.
Each step smaller from f/1.4 to f/2.0 to f/2.8 to f/4.0 and son on is a reduction ofthe light to half for each step. The Noctilux f/1.25 therefore lets 50% more light in through the lens than a 75/1.4 Summilux.
f-stop = the ratio of the focal length (for example 50mm) of a camera lens to the diameter of the aperture being used for a particular shot. (E.g., f/8, indicating that the focal length is eight times the diameter of the aperture hole: 50mm/8 = 6,25 mm); or the other way around, the hole is the focal length divided with 8).
ORIGIN early 20th cent.: from f (denoting the focal length) and number.
One f-stop is a doubling or halving of the light going through the lens to the film, by adjusting the aperture riing. Adjusting the f-setting from f 1.4 to f.2.0 is halving the light that goes through the lens. Most Leica lenses has half f-stops to enable the photographer to adjust the light more precicely.
 The aperture blades inside the lens is clearly visible in this photo by Eolake Stobblehouse. The aperture blades inside the lens is clearly visible in this photo by Eolake Stobblehouse.
Flare = Burst of light. Internal reflections between (and within) lens elements inside a lens. Mostly, flare has a characteristic "space travel" look to it, making it cool. Particularly in older lenses with less or no coating of the glass surfaces to suppress this, it can be a really cool effect. In newer lens designs, the coatings and overall design try to suppress flare and any reflections to a degree, so that there is seldom any flare to be picked up (moving the lens to pick up a strong sunbeam), but instead a "milking out" (or "ghosting") of a circular area of the frame; meaning simply overexposed without any flare-looking flares.
 |
|
 |
Sunlight creating (fairly supressed) flare in the bottom right quadrant of the image of a modern lens. |
|
The camera moved slightly to avoid the flare. |
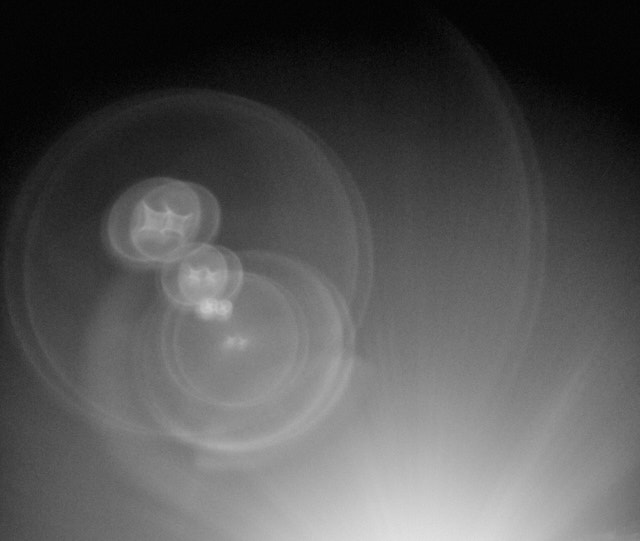

Older lenses with less coating, or without coating, are known to create flare that can look like this (Leica 50mm Summicron-M f/2.0 II Rigid model from the 1960's). © Thorsten Overgaard.

Lens flare in the movie, The Graduate (1967).

Lens flare in Mission Impossible Fallout (2019)

Lens Flare in Star Trek (2013). JJ Abrams famously said, "I know there's too much lens flare ... I just love it so much. But I think admitting you're an addict is the first step towards recovery (ha ha)"
|
Flickering = blinking light. This may result in "banding like" horizontal stripes in an image, or simply that the light you see isn't in the picture, or it looks different. For example, you take a photo in light, and the result you get is darker. You take another, and now it is all right. The reason is that some light blinks. Here's the difference within one second (notice how the light in the room, the wall light and the sign light all flicker):
 |
|
 |
| |
|
|
 |
|
 |
Flickering light causing different result in each frame becasuse the light blinks faster than the eye sees, but slow enough to be caught on camera. Here at shutter time 1/1500 sec, four pictures within a second.
Often you will see that you take a portrait indoor in an office, and from frame to frame the person has shade on one side of the face in one photo, but not the next. |
| |
|
|
Flickering ligh is a new challenge that photographers face, which is flicering light that looks good to the eye, but result in different results in a photo. Through cinema and photography history, the three standard high-quality light soruces have been daylight (from the sun), daylight HMI (5400 Kelvin Hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide lamps) and tungsten lamps (3200 Kelvin). When I say high-quality, it's because those are the light types that ensure high color quality (see the definition of CRI - Color Rendering Index in my "Leica and Photography Definitions page") and how quality light traditionally has a score above 90 CRI).
In recent years we have seen "light that flickers" because it has a pulse, such as stage light, photo lamps, video lights and of course indoor and outdoor late night lamps using LED (Light-emitting diode), compact fluorescent lightbulp-shaped lamps and other low-energy lamps (such as halogen). These light also generally have lower CRI (Color Rendering Index) below 90, and even lamps that are stated to have 90 CRI or higher, may mis out on the important red and blue tones, which will make it impossible to get the colors right, espoecially skin tones). If a stage has one or more low-quality lights (which they thend to have), these will pollute the colors of the scene to some degree.
| |
 |
| |
Banding as result of electronic shutter, and often also if the ISO is high. |
Flickering horizontal stripes (or "banding"-looking stripes) may appear when you use electronic shutter, and you are photographing with one or more light sources that flickers.
When the electronic shutter is on, you are usually at higher shutter speeds than 1/2000, which means there it would be possible to go down to a lower ISO, and to activater the mechanical shutter. (In some cameras you can choose to use electronic shutter throughout the entire range, which would make the camera completely silent; and this alone may cause horizontal stripes/banding if one or more lights in the room flickers).
Flickering in the EVF is very normal and will apear often without the vertical lines you see in the EVF will be in the picture.
| |
 |
| |
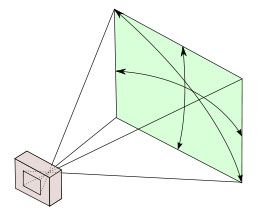
A 28 mm lens has a 74° viewing angle |
| |
|
Focal length = Originally focal length referred to the distance from the sensor (or film in older days) to the center of focus inside the lens (28mm, 50mm, 400mm, etc). Today one call it effective focal length (EFL) as a 400mm lens is not nessesarily 400mm long due to optical constructions that can make it shorter. The 35-420mm zoom on the Leica V-Lux 1 is for example only ca. 135 mm long. Nobody uses that measurement, except those who construct lenses! For users of lenses, focal length refers to how wide the lens sees. The viewing angle, which is often given in for example 90° viewing angle for a 21mm lens, 74° viewing angle for a 28mm lens, 6° viewing angle for a 400mm lens, etc.
Each human eye individually has anywhere from a 120° to 200° angle of view, but focus only in the center.
Focus, in - Sharp and clear in appearance. Focus - “The burning point (of a lens or mirror)”. In Latin the word focus meant fireplace or hearth. The word was probably first employed outside of its Latin literal use as “the burning point of a lens or mirror” in optics, and then came to mean any central point. The German astronomer Johannes Kepler first recorded the word in this sense in 1604.
| |
 |
| |
Full Frame is "king of photography" |
| |
|
Full Frame (FF) = The size of the sensor is 24 x 36mm which is the format Oskar Barnack and Leica Camera AG invented with the first Leica that was introduced in 1925. Many other formats invented since, such as APS, APS-C and all usually refer to Full Frame ratio, by which it means what size they have compared to Full Frame. The "full frame" technically deifinition thouhg is a sensor that camtures the full frame in one go (as the early sensors as in Leica S1 scanned the image/senor over a period of time).
The 24 x 36mm Full Frame format is so "king of photography" that it has continued to be the ideal for all cameras. Besides this, there exists Large Format cameras such as 4x5" (100 x 125 mm) and Medium Format 6x6 (60 x 60mm amongst other sizes in that area).
Ghosting = Secondary light or image from internal reflections between (and within) lens elements inside a lens. The reflected light may not always be in focus, so overall it looks like a "milked out" image. A subject in focus has brightened patches in front of it that come from reflections inside the lens. the most elementary look of ghosting is when you look in a rear-view mirror in a car at night and you see doubles of the headlights behind you (a strong one and a weaker one), because the headlights are reflected in a layer of clear glass on top of the mirror glass.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| Degrees of ghosting from strong sunlight entering from outside the frame. To the right the outside light has been shielded with a shade. |
| |
 |
| |
The Hektor 73mm f/1.9 of 1930-1931 sells at $900 - $6,000 these days. |
| |
|
Hektor - Refers to the maximum lens aperture - usually f2.5 (whihc at the time of development in the 1930's was considered very light-strong lenses). The name was apparently taken from the name of lens designer, Professor Max Berek's dog, Hektor. He also had another favorite dog, Rex, which may have inspired the lens name Summarex.
But ...
there is also another possibility, which is that Hektor (the lens and/or the dog) was inspired by Hektor, the oldest son of the Trojan king Priamos, who is listed in the history books as being the most couragerous defender of his home city, Troy. (Max Berek knew of this because Greek history had been required during his high school education).
In any case, the first 50mm Hektor f/2.5 was designed by Max Berek in 1931 for the Leica I Model A, and the - for that time - extremely light-strong 73mm Hektor f/1.9 was designed in 1930-1931 in preparation of the modular Leica system.
Hue = A color or shade depending on the dominant wavelength of red, green or blue. The word Hue comes from Swedish hy which is "skin complexion". It is independent of intensity, so often (in computer editing programs for example), Hue is an adjustment along Saturation which is (intensity of color as compared to white)
ISO = Light sensitivity of the camera sensor is given in ISO (International Organization for Standardization). It's a standard that was used in film and is now used in all digital cameras also. The base ISO for the Leica TL2 sensor is around 100-150 which means that this is what the sensor "sees". All other levels are computer algorithms calculating the effect as if the sensor could "see" more (hence noise at higher ISO levels).
ISO goes in steps of doubling: When the ISO is raised from 100 ISO to 200 ISO, the camera only need half the amount of light to make the same picture. For each step in ISO to 400, 800, 1600, 3200, etc. the light sensitivity is doubled for the sensor (and the camera sensor only need half the light of the previous ISO to record the same image).

6400 ISO indoor photo. With modern cameras the ISO can go to 3200, 6400, 12,800 and even higher without loss of dynamic range and without digital noise. Leica M10 with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
JPEG = A standard for picture format made in the 1990's by Joint Photographic Experts Group). Mostly referred to as JPG as in L1003455.JPG which would be the name for a JPG file from the camera.
Leica = A compound word derived from " (Lei)tz" and "(ca)mera". Apparently they were originally going to use "LECA", but another camera company already used a similar name in France, so they inserted the 'i' to prevent any confusion.
Lens - A piece of glass or similarly transparent material (like water or plastic). It has a shape so that it can direct light rays. The word “Lens” is used both for single piece of glass as well as a camera lens with several lenses that works together. From ‘lentil’ because similar in shape.
Lens hood = (also called a Lens shade). A tube or ring attached to the front of a camera lens to prevent unwanted light from reaching the lens and sensor. In the past where lenses were not coated to prevent internal reflections inside the lens, the lens hood was often essential. These days where lenses are coated, the shade serves just as much as decoration and protection (bumper) as well.
ORIGIN Old English hod; related to Dutch hoed, German Hut 'hat,' also to hat.

Lens hood or Lens shade attached to the front of the lens to prevent light rays from the side to hit the optics, which could introduce unwanted light and hence reduce contrast of the image. These days where lenses are coated, the shade serves as decoration and protection as well.
| |
 |
| |
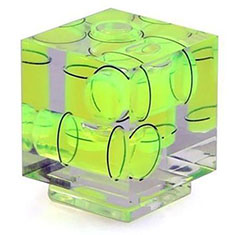
Bubble Level Gauge to mount onto the flash shoe. |
| |
|
Level Gauge = This is a tool in the viewfinder to see if you hold the camera 100% horizontal and/or vertical. You can turn it on in the Menu > Photo Live View Setup > Level Gauge > On.
Before level gauge was integrated as a digitized feature in modern digital camers, it was a Bubble Level Gauge / Spirit Level you put on top of the camera.
The idea is to be able to get 100% vertical and horizontal lines (because if you tilt the camera slightly, the horizon will not be horizontal, and of you tilt the camera forward or backwards, the lines of for example vertical buildings will not be vertical.
 Digitized level gauge in a Leica M10-P. You tilt the camera up and down (front/back and left/right) till the level is completely straight. Digitized level gauge in a Leica M10-P. You tilt the camera up and down (front/back and left/right) till the level is completely straight.
Light = Tiny particles called photons that behaves like both waves and particles. Light makes objects visible by reflecting off of them, and in photography that reflecting off of subjects is what creates textures, shapes, colors and luminance. Light in its natural form (emanating from the sun) also gives life to plants and living things, and makes (most) people happier. So far, nobody has been able to determine exactly what light is. The word photography means “writing with light” (photo = light, -graphy = writing). Read more about light in my book Finding the Magic of Light.
Leica Thread-Mount (LTM): Also known as M39, is the screw mounted lenses for Leica cameras. It’s a simple as that; you screw on the lens, and back in 1932, the possibility to change the lens was the big news. The M39 system was updated with the M Bayonet from 1954 for the Leica M3. The M bayonet is a quick way to change lenses and is the current mount for Leica M digital rangefinders.
M (as in "M3", "M6", "M7" etc.)
A) The M originally stands for "Messsucher", which is German "Meßsucher" for "Rangefinder". The "3" in M3 was chosen because of the three bright line finders for the 50, 90 and 135 mm lenses. Later the numbers of the M cameras were more or less chosen to follow each other.
M-body evolution in chronologic order:
M3 - MP - M2 - M1 - MD - MDA - M4 - M5 - CL - MD-2 - M4-2 - M4-P - M6 - M6 TTL - M7 - MP - M8 - M8.2 - M9 - M9-P - MM (black and white sensor) - ME (Type 220) - Leica M (Type 240) - Leica M-P 240 - Leica M 246 Monochrom - Leica M-A (type 127, film camera) - Leica M 262 - Leica M-D 262 (without a screen) - Leica M10 - Leica M10-P.
B) M also refer to M-mount as the M bayonet that couple the Leica M lenses to the Leica M camera. Before the M bayonet the coupling between the camera and lens was screwmount.
C)
M nowadays refer to the Leica M line of cameras rather than the "Messsucher".
M9
Leica M9 is a model name for the Leica M9 that was introduced on September 9, 2009 (as the first full-frame digital Leica M). It was the latest model designation using the M and a number. From their next model, Leica Camera AG introduced a new model system so each camera would simply be a Leica M but then with a model designation like Typ 240, Typ 246, Typ M-D 262 and so on. The idea was inspired from Apple who name their computers for example MacBook Pro and then it has a sub- model number designation which model it is (and which would define speed of processor, etc).

Leica M9
Mandler, Dr. Walter (1922 - 2005)
Legendary Leica lens designer and CEO of Ernst Leitz Canada (ELCAN) 1952-1985. Read more in Leica History.
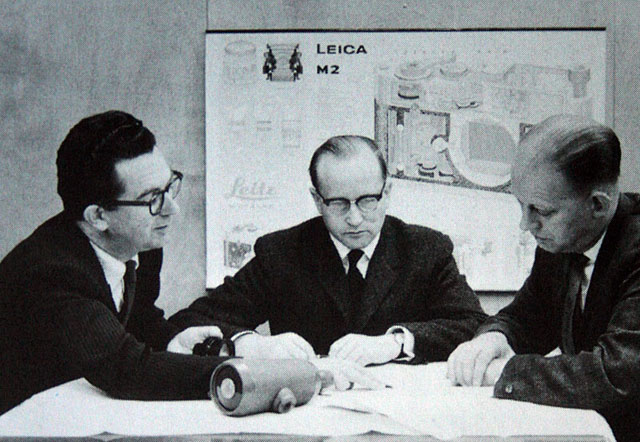

Dr. Walter Mandler (center) at the Ernst Leitz Camera factory.
Megapixel (or MP) - Millions of pixels. See pixel further down. How many units of RGB is recorded by a given sensor by taking height x widt. A Leica M10 delivers a 5952 x 3968 pixel file = 23,617,536 piexls. On a screen the resolution you choose determines the size of the image. Say you have a 5000 pixel wide file and your screen is set for 8000 pixels wide. Then the image will fill only the 5000 pixels fo the 8000 and the rest will be empty, If you then change the screen resolution to 5000 wide, the image would be able to fill out the whole screen.
Meßsucher = (rangefinder or distance finder) = Mess = range, sucher = finder. It is always correctly written with the "ß". There are technically not three "s", rather the "ß" and one "s" because it is a word constructed by the combining of two precise words.
MF (Medium Format), as in the Leica S System.
MF (Manual Focus) for lenses that are focused by hands, as opposed to Auto Focus.
mm = millimeter(s), as in a 50mm lens. (Earlier in lens history lenses focal length was given in cm = centimeters; as in a 5 cm lens). For anyone used to centimeters and millimeters, it’s no wonder. But if you grew up with inches, feet and yards, you may have had a hard time grasping what a 50mm lens was. But as lenses were designed first in Europe, the metric system with centimeters and millimeters was used to describe lenses.
The reason a 50mm lens is a 50mm lens is that there is 50mm from the focus plane (the film or sensor) to the center of focus inside the lens. When photography was a young subject, it was engineers who made it all, and the users were expected to understand. The engineers were so into the making of the lenses, that it apparently never dawned upon them that today’s users would think of a 21mm lens as a wide angle lens rather than a lens where there is 21mm from the sensor to the center of focus inside the optics.
MP
a) Stands for Mechanical Perfection, as in the Leica M-P.
b) Megapixels (millions of pixels).
c) Megaphotosites (millions of photosites).
ND
Neutral Density filters are grey filters function as 'sunglasses' for lenses. They simply block the light so that a lens can work at for example f/0.95 or f/2.0 in sunshine.
If a camera is set to 200 ISO and the maximum shutter speed is 1/4.000, this will usually result that the lens has to be at f/2.8 or smaller aperture in sunshine. Else the image will over-exposed. So in order til stay within the maximum shutter speed of 1/4.000 and still use a lightstrong lens wide open, one mount a ND-filter that reduce the light with 3 stops (8X) or 6 stops (64x).
For video ND-filters are used quite a lot (as the shutter speed for video is 1/60), and ND-filters are also used to reduce the light for really long multi-exposures at night (stop-motion video and stills).
ND-filters also exist as variable ND-filters so one can adjust the amount of light going through from for example 1 stop (2X) to 6 stops (64X).
ND-filters also exist as graduated ND-filters where the top of the filter is dark and then gradually tone over in no filter (so as to reduce the skylight in a landscape for example).
The ND filters are called Neutral because it is a neutral filter. It doesn't change colors, only the amount of light.
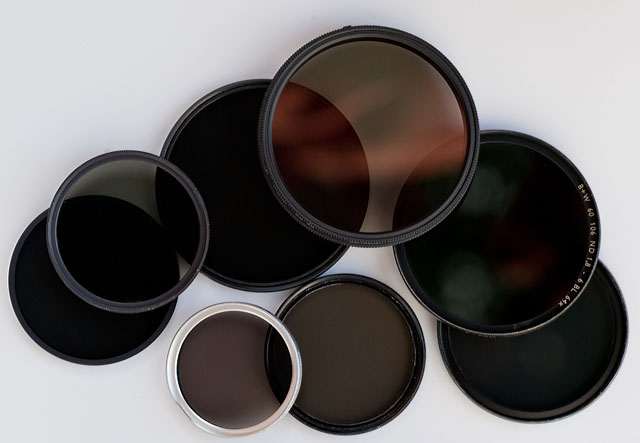

ND-filters / gray-filters.
"Niner"
The nick-name for the 90mm f/2.5 Leica lens in the 30's when it first came out.
Noctilux = Also known as "King of the Night" because "Nocti" means Night and "Lux" means Light. The f/1.0 lenes from Leica are named "Noctilux". The first Leica Noctilux lens was the 50mm Noctilux f/1.2 which shortly after it's introduction was improved to the 50mm Noctilux f/1.0. In the current model the f-stop has been improved further to f/0.95.
"Noctilux" refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f1.0 . "Nocti" for nocturnal (occurring or happening at night; ORIGIN late 15th cent.: from late Latin nocturnalis, from Latin nocturnus ‘of the night,’ from nox, noct- ‘night.), "lux" for light. The Leica Noctilux 50mm f1.0 is famous for enabling the photographer to take photos even there is only candleligts to lit the scene. See the article "Noctilux - King of the Night"

The Noctilux "King of the Night" lens. From left the f/0.95 in silver (same on the camera, in black), the f/1.0 in the back and the rare and expensive first model, the f/1.2 in the front.
No.
Number, on this site Leica catalog numbers or order numbers. Some the numbers changed depending on the number of cams in the lens: The Elmarit-R f2.8/135mm started life as No. 11 111, however when fitted with 2 cams for the SL became No. 11 211, yet another No. for the 3 cams lens and a fourth number for 3 cam only at the end of its life. Number changes also applied to M lenses depending on whether they were screw-thread, bayonet or for M3 with “spectacles”. Thus the No. in the Thorsten Overgaard Leica Lens Compendium list is a guideline but not a comlete list of existing catalog numbers.
Optic = Eye or vision. From French optique or medieval Latin opticus, from Greek optikos, from optos ‘seen.’
Perspective = The way objects appear to the eye; their relative position and distance. Also, selective focus (foreground and background out of focus) can change the perception of perspective (also see Three-dimensional). A wide angle "widens" the perspective and makes objects further away appear smaller than they are to the eye; and objects closer, relatively larger than they are to the eye. A tele lens will "flatten" the perspective and often objects further away will appear relatively larger than close objects than they are in real life. A 50mm lens is the one closest to the perspective and enlargement ratio of the human eye.
The word Perspective comes from the latin word for optics (perspicere, per- ‘through’ + specere ‘to look’), and so-called Renaissance painting is simply painting done within the framework of optics and the linear perspective it presents.
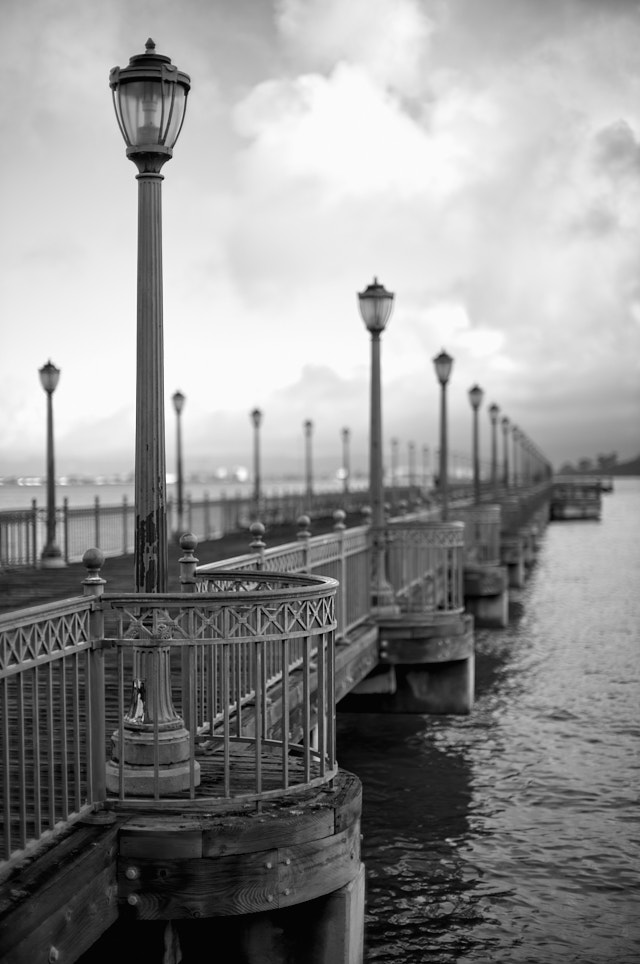

Perspective is relative position and distance. The objects nearby are larger than objects far away. This is how the eye and the mind calculate distance. The eye and the camera automatically captures perspective. In darwing and painting one would see "stupid" two-dimensional drawings 500 years B.C where elements were thrown into the mix without considering that a an object far away must be smaller than if close to the viewer. The word "perspective" comes from "to look through (optics)". Pier 7 in San Francisco by Thorsten Overgaard. Leica M11 with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95.
| |
 |
| |
Vanishing points are the points where lines meet. This is how you make perspective in paintings and drawings (and some times make movie sets or theatre stages appear more three-dimensional than they are) |
| |
|
Painters works with vanishing points, which is where the lines meet, so as to create an illusion of perspective and three-dimensional effect on a two-dimensional painting or drawing.
The human eye corrects for perspective to an extreme degree. We always see vertical lines vertical and horisontal lines horisontal: The eye has a angle of view equivalent to an 8mm wide angle lens, a size ratio equivalent to a 50mm lens and we focus on relatively small area of the viewing field - one at the time. Three things happens that are worth paying attention to:
1) We compile areas of our view that we focus on, to one conceptual image that "we see". Ansel Adams, the great American landscape photographer pointed out that a large camera used for landscape photography capture every detail in focus and sharp so you can view it in detail after; but the eye does not see everything in focus when you try to compose the landscape photography, the eye scans only one part at a time and stitch the idea together. This makes composing or prevision of a landscape photography challenging.
2) We compile areas of our view that we individually adjust the exposure of. A camera adjust the exposure of the whole image frame to one exposure. That's why what looks like a nice picture to the eye of houses in sunshine with a blue sky above, becomes a photograph of darker buildings with a bright white sky: The camera simply can't take one picture that compare to what we "compiled" with our eyes, adjusting for each type of light.
3) Objects (on a table, for example) in the bottom of our viewing field will appear 100% perspective corrected - to a degree that it is impossible to correct in optics, with or without software correction. A wide angle lens, even with little distortion, will exaggerate the proportions of the closet part so it - to the eye - looks wrong.
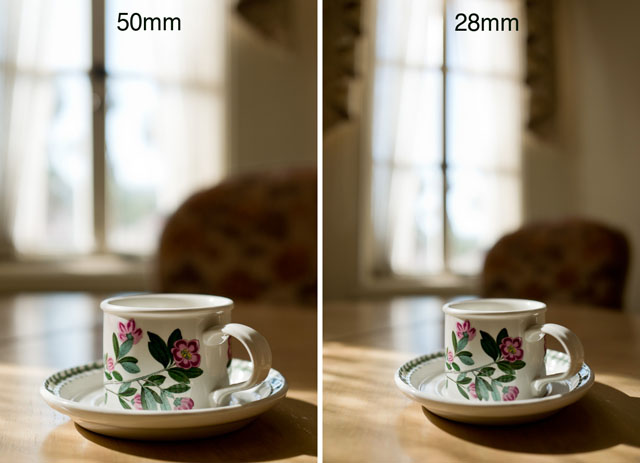

Perspective distortion: Comparing these two photographs you can see how the cup stretches in the 28mm wide angle photograph compared to the 50mm photograph. Both actually has a little stretch because both the cup is in the edge of the frame in both photographs. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Perspective correction - In software like Adobe Lightroom and Capture One Pro there is often a feature to correct perspective (and distortion) like seen below. You can change perspective this way, or at least make believe: If you correct a tall building on teh vertical lines, you will notice that the height of the windows doesn't match the perspective. If the building is with straight lines, the windows should all be of the same size. But a tall building seen from below and corrected with software will have taller windows (closer to camera) in the bottom than in the top (further away from the camera originally).
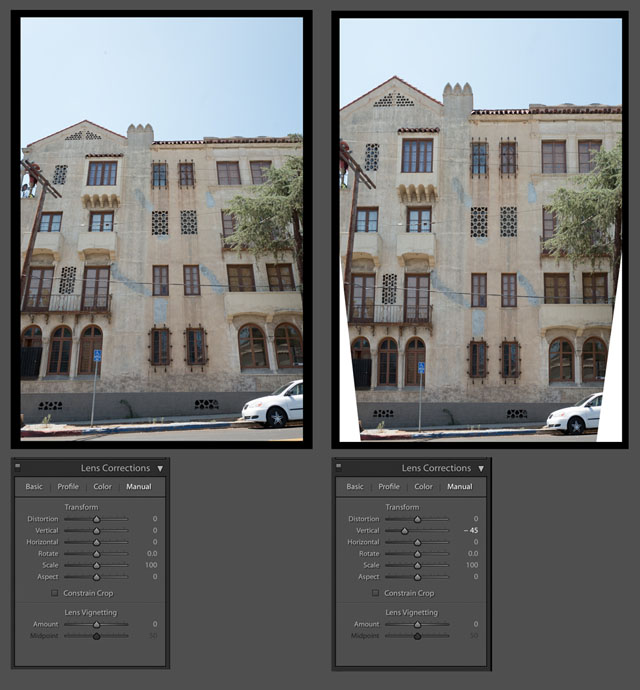
Perspective correction in Adobe Lightroom. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
| |
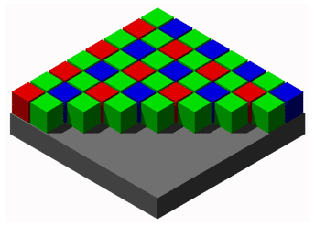 |
| |
A graphic illustration of the typical Bayer Color Filter Array on an RGB sensor. It's called a Bayer filter because Bryce Bayer of Eastman Kodak invented the technology of filtering incoming light into RGB and distribute it into the the photosites that each read just one color (R/G/G/B). |
| |
|
Photosite - The unit in a digital camera sensor that records intensity of either red, green or blue. Unlike the output of a sensor, measured in pixels (and where each pixel contains RGB), the photosite records only one color each, and it's intensity (how bright it is). A photosite can not distinguish colors, which is why there is a Color Filter Array (basically a prism) above them to filter the colors and send information to the photosite if 's a R, G og B color. See illustration below. In a monochrome sensor (as in the Leica M Monochrom and the Phase One Achromatic), all photosites are recording intensity of light only as there is no concern which color it is, and there is no color filter.
The ratio of photosites to pixels is not a given. Each block of 4 contiguous photosites contains one photosite sensitive to low wavelengths (blue), one photosite sensitive to high wavelengths (red), and two identical photosites sensitive to medium wavelengths (green). So four photosites would be the minimum to create one 'full-color' pixel. Apart from that, depends on the sensor specifications, which is different from brand to brand. Sometimes four photosites (two Green, one Red and one Blue) makes up one pixel, at other times it's more photosites to one pixel; and there is also pixels sampled from photosites across (sort of overlapping patterns).
Pixel - Made up word from Pix (picture) and el (element). A pixel is the smallest full-color (RGB) element in a digital imaging device. The physical size of a pixel depends on how you've set the resolution for the display screen. The color and tonal intensity of a pixel are variable, meaning that each pixel contains RGB. This is different from a camera sensor's small eyes (photosite) that are an intensity of either red, green or blue. You could say that the digital sensor's photosite (where each unit collects just one color; red, green or blue) is the input technology, whereas the pixels on a screen (where each pixel contains red, green and blue) is the output device. So while sensors are measured in megapixels (mega = million), it's their output unit of pixels, and not the input unit of photosites that is measured and stated. See illustration below.
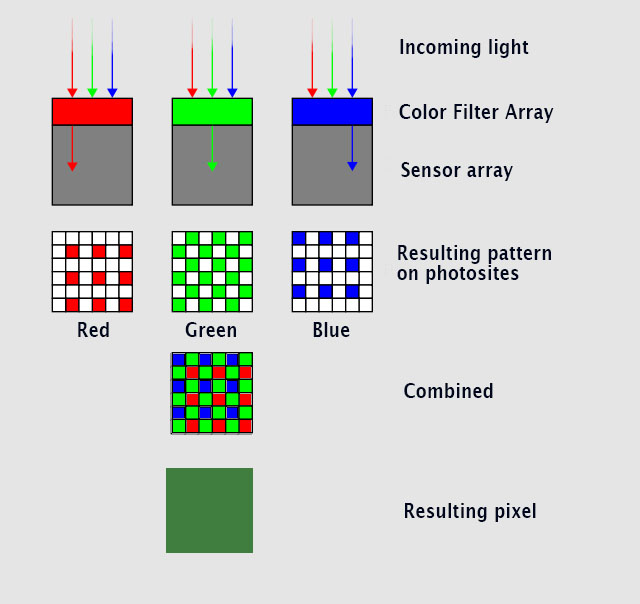
Here's an illustration of how light goes through a color filter that enables the underlying photosites to each record if it';s an R, G or B color - combined - makes up one pixel containing RGB. © Thorsten Overgaard.
RF
(R)ange (F)inder - the mechano-optical mechanism which allows M Leicas to focus.
Alternative meaning - RF is also shorthand for Hexar RF , Konica's motorised "M-lens-compatible" rangefinder camera released in 2000.
S = Single image. When the ring by the shutter release on top of the camera (or in the menu of a digital camera in case it does not have this ring on the ourside) is moved from OFF to S, the camera takes only one photo at the time (Single). The other possibility is Continuous where the camera takes pictures continiously as long as the shutter release button is helt down. (see above).
Saturation: How colorful, intense or pure the color is. Less saturation would be less colorful, more saturation would be more colorful. In today’s photography, de-saturating a photo on the computer will gradually make it less and less colorful; and full de-saturation would make it into a black and white photo.

A photo from Verona, Italy de-saturated, normal saturated and over-saturated. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Sensor = A device that detects a physical property (like light) and records it. A camera sensor is a plane plate with thousands of small “eyes” with (photosites) a lens in front of each (CFA, Color Filter Array), which each individually records the amount of red, green and blue light rays that comes through the lens. Together, Red, Green and Blue form all colors of the spectrum, which becomes a pixel. Sensor comes from Latin sens- ‘perceived’.
SDC = Software Distortion Correction. A correction of lens distortion (not straight lines) applied in the camera and which is part of the DNG or RAW file. In Lightroom or Capture One Pro the SDC of the camera file is applied automatically (and cannot be removed), in software like AccuRaw one can open the DNG file without the SDC correction. Sean Reid Reviews have written a good article on what SDC is and does in "Software Distortion Correction".
SDC (Software Distortion Correction): In Lightroom the correction profile for the Fujinon 23mm is applied automatically and cannot be turned off. If you go into Develop mode in Lightroom and look under Lens Correction > Profile, you will see a message in the bottom with an exclamation mark. When you click on that, you get the message above.
Sharpness - See “Focus”
Shutter speed dial - The dial on top of the Leica M where you can set the shutter speed manually. It can also be set to A which stands for Aperture Priority (where the camera suggests a shutter speed; or when you move the dial away from A, the camera will show arrows in the viewfinder, suggesting which direction to change the Aperture to, to get the correct exposure).
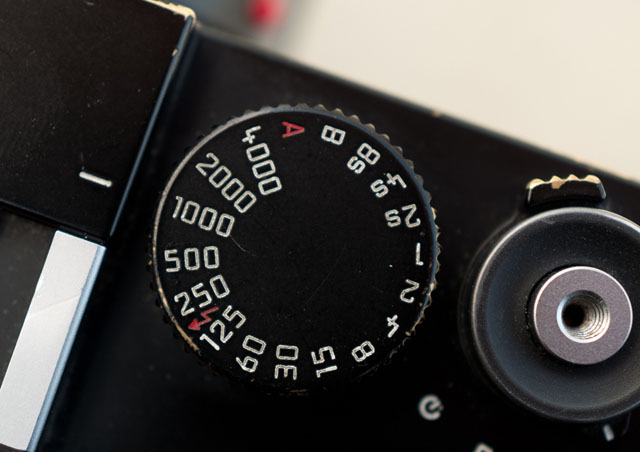

Shutter speed dial set to 1/1000 of a second.
SLR = Abbreviation for Single-Lens Reflex; the lens that forms the image on the film/sensor also provides the image in the viewfinder via a mirror. Newer camera models has aen EVF (Electronic Viewfinder) that displays in the viewfinder what the sensor sees in real-time.
| |
 |
| |
Leitz Wetzlar Mikro-Summar 42mm f/4.5 lens anno 1910 might be the first lens carrying the name Summar. |
Summar - (or a story of name development)
The 1933 lens 50mm f2.0 Summar: It started out as Summar(f2.0), then the Summitar (f2.0 in 1939), then the Summarex(f1.5 in 1948), then the Summaron(35mm f.2.8 in 1948, then later f2.0, f3.5 and f5.6 lenses), then the Summarit (f1.5 in 1949 and used again for the 40mm f2.4 on the Leica Minilux in 1995, then again for the 35mm, 50mm, 75mm and 90mm Summarit f2.5 in 2007) then the Summicron(f2.0 in 1953 for the collabsible 50mm) and finally the Summilux(50mm f1.4 in 1959).
ORIGIN of Summar is unknown.
Summarex
The great thing about being a lens designer is that you get to name the lens. Dr. Max Berek who worked for Leitz from 1912 till his death in 1949 named lenses after his two favorite dogs. One was Sumamrex named after his dog Rex, the other Hektor named after his dog Hektor.
Summarit
Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f/1.5.
Summicron = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f/2.0 . There are many guesses how this name came about, a popular one being that the "summi" came from "summit" (summit means the highest point of a hill or mountain; the highest attainable level of achievement) while the "cron" came from "chroma" (ie. for colour). Not so: The name (Summi)cron was used because the lens used Crown glass for the first time, which Leitz bought from Chance Brothers in England. The first batch of lenses were named Summikron (Crown = Krone in Deutsch). The Summi(cron) is a development from the orignal Summar (the 50mm f2.0 lens anno 1933). Vario-Summicron, Vario-Elmarit is Leica Camera AG's name for zoom lenses, for example the Vario-Summicron f/2.0 as the one that is on the Leica Digilux 2.
Summilux = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f/1.4 , "-lux" added for "light" (ie. the enhanced light gathering abilities). In Leica terminology a Summilux is always a f/1.4 lens and a Summicron is a f/2.0 lens.
Telyt
Lens nomenclature - short-hand for " telephoto " (tele- is a combining form, meaning to or at a distance) and used in names of instruments for operating over long distances : telemeter. The name has been used for a number of tele lenses from Leica.
ORIGIN: from Greek t?le- ‘far off.’
Televit
rapid-focus device from Leitz that was made from 1966 through 1973, in both R and VisoflexIt was originally designed for use with the 400mm f5.6 Telyt and 560mm f5.6 Telyt. Beginning in 1970 (with serial 2340953) the Televit could also be used with the 280mm f4.8 Telyt-V by using adapter 14138.
Thambar
Leitz Thambar 90mm f.2.2. At most about 3000 were made, probably in eight batches, starting with 226xxx (actually built in 1934) and going through 283xxx, 311xxx, 375xxx, 416xxx, 472xxx, 511xxx, and 540xxx (about 1939/1940).
Today they are staggeringly rare and extremely expensive: you would be lucky to get away with much less than $1500 for the lens without accessories (center spot, shade, cap), and you could easily pay twice that for a good, complete example with clean glass.
Known to be a legendary soft-focus portrait lens that 'make a woman look 10 years younger.' A glass filter with a black spot in the middle, about 13mm (1/2”) in diameter cuts out the central (sharpest) part of the image and makes everything even softer.
(Source: Roger W. Hicks)
Here are some advice from a Thambar user, Theodor Heinrichsohn, who have used it mainly for portraits using an Leica M5 and Leica M6:
1. The results are more or less unpredictable. Best practice is to shoot many times and pick the one you like best.
2. Shots against the light are generally more effective than with the light behind you.
3. The most pleasing results to my taste were with center filter at medium apertures. With luck portraits took on the "dreamy" look that the lens is famous for.
4. I never used the Thambar for anything except portraits.
The lens has been rumored to be slightly radioactive due to the process of producing the glass.
Here are some sample photos of Koichiro Itamura Photography.
Here are some more sample images from Blue Penguin.
Origin of the name is currently unknown. Suggestions has been made that the name Thambar was derived from Greek, meaning “something that inspires wonder”. Also close to the English word Tamper (with) which is to meddle, damaging or altering something.

A complete set of a Leitz 90mm Thambar f/2.2 consist of the original red box, lens cap, lens shade and the special soft focus filter with a black dot in the middle. They exist in both a Meter and a Feet edition (the focusing scale). Only 3,500 or less were made from 1934-1940, from serial number 226001 to 540500. Read my article on Leica 90mm lenses.
Thick / Thin
The first 90mm Elmar that came out in 1930 was called "Thick" of "Fat" When the smaller Elmar came out in January 1933 it was called "Thin".
Three-dimensional = Having the three dimensions of height, width and depth. In photography and lens design, three-dimensional effect is also the perception of even small micro-details; the texture of skin can appear flat and dead or three-dimensional and alive. Also, selective focus (foreground and background out of focus) can change the perception of depth. Also see Perspective.

Three-dimensional = Having the three dimensions of height, width and depth. Melrose Avenue in Los Angeles. Leica TL2 with Leica 35mm Summilux-TL ASPH f/1.4. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
Ventilated Shade - A shade is a hood in front of a lens that provides shade from light going straight onto the lens from outside what you are photographing, which could cause internal reflections like flare, which would make the picture less contrasty.
The ventilated shade has holes so it doesn't obstructs the view from the viewfinder. In many of today’s mirrorless cameras where there is no viewfinder looking ver the lens, so there is no actual need for a ventilated shade; but they are considered classic or vintage looking and are still in high demand. It makes no difference for the purpose of the shade (to create shadow) if it is ventilated or not.

Ventilated Shade for the Leica Q. I make ventilated shades for most lenses and sell them from here.
Viewfinder a device on a camera showing the field of view of the lens. Also known as the German word "Messucher" (or Meßsucher).
1) A built-in viewfinder in a camera that simply show the frame you get when you look through the viewfinder.
2) A rangefinder viewfinder which is also used to focus the lens. In Leica M cameras two pictures has to meet and lay 'on top of each other' for the picture to be in focus.
3) An external viewfinder, usually on top of the camera in the flash shoe, so as to show the field of view of lenses vider than what the built-in viewfinder can show (15mm, 21mm, 24mm, 28mm etc viewfinders exist)
4) Very simple "aiming-devices" on top of a camera that is simply a metal frame without any optics. Just a frame, as for example very old cameras (the original Leica), or when using cameras in diving where you can't look through the camera.
5) A Electronic Viewfinder (EVF) that shows what the sensor sees "live".
Visoflex
A device mounted between the Leica M camera and a lens, containing a mirror mechanism like in a SLR camera, thus allowing the M user to 'preview' a picture using a tele lens larger than 135mm which is the maximum covered by the framelines in the Leica viewfinder.
Ø - Diameter. As in Ø49 for example which means that the filter diameter is 49mm for this lens (or if a filter is Ø49, it is 49mm in diameter and fits that Ø49 lens). Leica uses E to express their filters sizes, as in E49 for a 49mm filter size.
To be continued ...
Suggestions for further reading ...
Facebook Leica M Monochrom User Group
"Henri - The Leica M Monochrom" article by Jono Slack who - likewise as he did with the Leica M9 prototype back in 2009 - took the prototype Leica M Monochrom to China and made a beautiful simple article about his experiences. Jonathan Slack has also made some of his DNG files available. May 2012.
Ming Thein does some very interesting reviews and have started a three-part of the "Leica M Monochrom review" on his blog. May 23, 2012.
White Smoke Studio blog with wedding photographs taken with the Leica M Monochrom
Erwin Puts has made a very short and precise account of what kind of milestone the Leica M Monochrom and the accompanying new 50mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH f/2.0 lens is. His "Leica Monochrom" article is here. June 2012l
Also Sein Reid Reviews www.reidreviews.com have had the Leica M Monochrom prototype out for testing and have written a good review. This is for subscribers so you may want to subscribe (33$ per year).
David Farkas have done a review as well on the Red Dot Forum of the Leica M Monochrom. He has also done a ISO comparison between the Leica M9 and Leica M Monochrom.
Luminous Landscape also have tested the Leica M Prototype and have written about it here. May 15, 2012.
Steve Huff and guest readers also have written about the Leica M Monochrom.
The street photographer and blogger Eric Kim has written an article about Leica M Monochrom for street photography.
Last, but not least, British based World Press winning photographer and Leica M9 shooter Edmond Terakopian have written the blog post "The King of the Tones?" with a short hands-on review.
|
![]()
