Leica 35mm Definitions:
| |
 |
| |
1:2/50 the description says.
But what does it mean? |
| |
|
1: = Basically means 1 divided with. On the lens to the right, it means that the diameter of the hole throught he lens is 25mm.
We would normall call it
a 50mm f/2.0 lens. The writing of 1:2/50 is a tradition from the 1800's of specifying a lens, which reveals quite a bit about the construction:
Focal length 50mm simply means that the distance from center of focus inside the lens to the focusing plane (the sensor or film) is 50mm, and the aperture of f/2 or 1:2 means that the diameter of the hole the light comes throught is 25mm (50mm divided with 2 = 25mm).
In traditional lens design, one could usually tell from looking at the length of a lens if it was a 400mm, 100mm or 35mm. Newer designs with mirrors (in tele lenses) and more corrections (in wide lenses) can make the size of the lenses shorter or longer, but the distance from center of focus to sensor in a modern 50mm lens will still be 50mm for a 50mm and 400mm for a 400mm, and so on.
See Focal length and Aperture further down for more.
35mm
a) 35mm lens is a lens that has a viewing angle of view is 63°vertically, 54° horizontally and 38° vertically within a 35mm film frame or "full-frame" 24x36mm digital format. See Focal length further down.
b) 35mm focal length: the distance from center of focus inside the lens to the focusing plane (the sensor or film) is 35mm.
| |
 |
| |
35mm film format (also known as full-frame) |
| |
|
c) 35mm film format (also known as full-frame in digital sensors) was a standard film format that came about in 1892 where the width of the film roll was 35mm, and it's been the most used format ever since. Only a format of 24 x 36mm is used for the photo on the film roll.
35mm film format was first used in 1892 by William Dickson and Thomas Edison for moving pictures with frames of 24 x 18mm, using film supplied by George Eastman (Kodak), and this became the international standard for motion picture negative film in 1909. Later other motion picture formats came about, such as Academy Ratio (22 x 16 mm), Widescreen (21.95 x 18.6 mm), Super 35 (24.89 x 18.66 mm) and Techiscope (22 x 9.47 mm).
The inventor of the Leica camera, Oskar Barnack, built his prototype Ur-Leica in 1913 as a device to test film stock and\ motion picture lenses and had it patented. Putting 35mm film format into a small camera gave him the idea "small negative, large print" and he decided to increase the size of each frame on the 35mm film to 24x36mm (for more detail and sharpness), and then invented an enlarger to make large prints from the small negative. The length of a film, 36 pictures, is said to have become the standard because that was how far Oskar Barnack could stretch his arms (when cutting film from larger rolls to put them into film rolls for the Leica camera).
d) 35mm equivalent is often given as a standard when talking about lenses in small compact-cameras or large format cameras with other sensor/film format than the 24 x 36mm frame. Example: A camera with a 12 x 18 mm sensor has a 14mm lens on it, and even the lens is actually a 14mm, it is specified as a 28mm lens because the viewing angle that ends up on the sensor is equivalent to a 28mm lens on a 35mm of full-frame camera.
AF = Auto Focus. The idea is that the camera does the focusing itself (the word auto comes from Greek "self").
Aperture = The same function as the iris and pupil has in the eye. The pupil in the eye is the dark circular opening in the center of the iris of the eye, varying in size to regulate the amount of light reaching the retina (the sensor area inside the eye).
Aperture on a camera is the f/ stop on the camera that regulates how much light passes through the lens by increasing or decreasing the hole through the lens. On a f/2.0 lens the lens is fully open" at f/2.0. At f/2.8 the aperture inside the lens make the hole through the lens smaller so only half the amount of light at f/2.0 passes through. For each f/-stop (4.0 - 5.6 - 8.0 - 11 - 16) you halve the light. The aperture of the lens is basically the focal length divided with the f/-stop = size of the hole (50mm divided with f/2.0 = the hole is 25 mm in diameter).
Besides regulating the amount of light (so as to match the correct exposure), the aperture also affects the dept of field: , which is how deep the sharpness is. To get the sough-after photos with narrow depth of field where the background is blurry, the lens has to be wide open at f/2.0 or so. Stopping the lens down to f/8 or f/16 will result on more depth of field, meaning the background will start becoming in focus. To maintain narrow depth of field, one can use the ISO sensitivity and/or the shutter speed to match the correct exposure (as aperture is only one of three ways to control the exposure; the correct amount of light).
ORIGIN: Late Middle English : from Latin apertura, from apert- ‘opened,’ from aperire ‘to open’.

The aperture blades inside the consist of a number of blades that - as the aperture ring on the lens is rotated - narrow into a smaller and smaller hole. © Thorsten Overgaard.
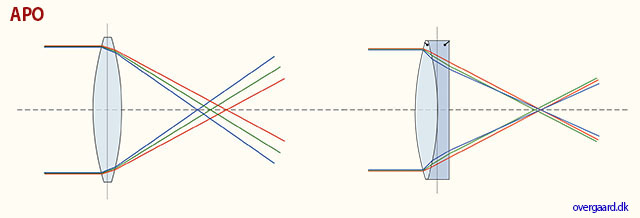
APO corrected basically means that the red, green and blue has been corrected to meet more precisely in the same spot. Clarity of colors and definition of details would be the result.
APO = in lens terminology stands for "apochromatically corrected". In most lenses, optical design concentrates the focus of blue light and green light into a single plane, but red light falls slightly into another plane of focus. In APO lenses, the design and expense has been put in to making red light focus on the same plane as blue and green. Under a microscope you would see that all light subject is now in focus, creating a sharper image overall. Many manufacturers offer APO designs, but in most of these only the very center of the lens is APO corrected. Leica prides itself on making most of the frame APO corrected.
APo-correction has traditionally been used for long tele lenses (and periscopes), but in recent years APO-correction has been applied to 50mm and wide angle lenses as well. One will notice that the colors are really bright and alive, almost more real than to the eye, in lenses like the Leica 90mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH f/2.0 and 50mm APO-Summicron-M ASPH f/2.0.
Apochromat; ORIGIN early 20th century, made of the two words; apo (Greek origin, away from) and chromatic (Latin origin, meaing relating to color).
| |
spherical (ball) |
| |

a-spherical (non-ball) |
| |
|
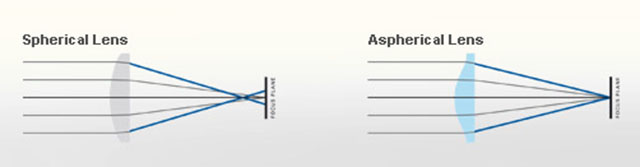
ASPH = (Aspherical lens) stands for "aspheric design".
Most lenses have a spherical design - that is, the radius
of curvature is constant. These are easy to manufacture by
grinding while "spinning" the glass. This design
however restricts the number of optical corrections that can
be made to the design to render the most realistic image possible.
ASPH lenses (a-spherical, meaning non-spherical), however, involve usually 1 element that does
*not* have a constant radius of curvature. These elements
can be made by 1) expensive manual grinding, 2) molded plastic,
or 3) Leica's patented "press" process, where the element
is pressed into an aspherical ("non-spherical")
shape. This design allows Leica to introduce corrections
into compact lens designs that weren't possible before. Practically,
the lens performs "better" (up to interpretation)
due to increased correction of the image, in a package not
significantly bigger than the spherical version.
There is another Aspherical lens manufacture technique: an uneven coating layer is applied to a spherical lens. The coating is thicker on the edges (or on the center, depending). Canon "Lens Work II" calls these "simulated" aspherical lenses. Simulated and Glass-Molded (GMo) asphericals show up in non-L Canon lenses, while the L lenses have actual ground aspheric elements.
A- means non, or without. From Latin, ex.
Sphere: ORIGIN Middle English : from Old French espere, from late Latin sphera, earlier sphaera, from Greek sphaira "ball".
| |
|
|
 |
| Normal spheric lens (grinded) |
|
ASPH (note the shape of the glass as result of pressing rather than grinding) |
Bokeh = The visual quality of the out-of-focus areas of a photographic image, especially as rendered by a particular lens: It's a matter of taste and usually photographers discuss a 'nice' or 'pleasant' bokeh (the out-of-focus area is always unsharp, which is why the quality discussed is if one likes the way it renders or not by a particular lens). The closer you get to something, the 'more' bokeh' you get (in that the focus becomes less for the background and foreground at close distances than at long distances). ORIGIN from Japanese 'bo-ke' which mean 'fuzzines' or 'blur.'.
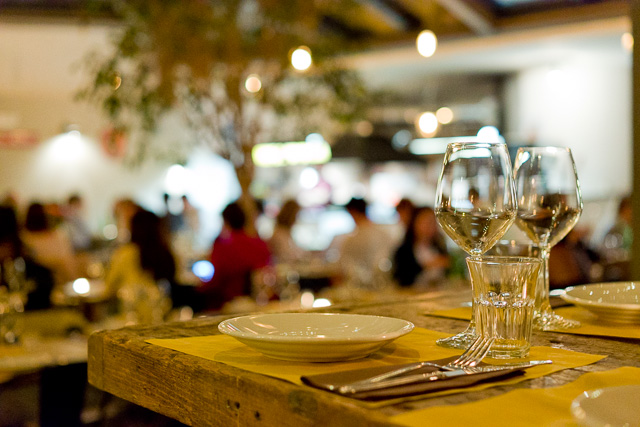 Bokeh: The visual quality of the out-of-focus areas of a photographic image. Photo at Bar del Fico in Rome. Leica TL2 with Leica 35mm Summilux-TL ASPH f/1.4. © Thorsten Overgaard. Bokeh: The visual quality of the out-of-focus areas of a photographic image. Photo at Bar del Fico in Rome. Leica TL2 with Leica 35mm Summilux-TL ASPH f/1.4. © Thorsten Overgaard.

Camera comes from Chambre, mostly in relation to Spanish soldiers’ rooms. Obscura means 'dark', so a dark room is basically the derivation for the word camera.
Camera - is today’s short name for Camera Obscura (meaning “a dark room”). Camera means Chambre and was used only as a Latin or alien word, actually only for Spanish soldiers’ rooms, until popularized in connection with photography in 1727: “Camera Obscura”. In 1793 the slang term “camera” was used by Sterne Tr. Shandy: “Will make drawings of you in the camera” and by Foster (1878), “The eye is a camera”. Camera Obscura was described by Iraqi scientist Ibn-al-Haytham in his book, “Book of Optics” (1021) and by Leonardo da Vinci in 1500; popularized and made widely known in 1589 by Baptista Porta when he mentioned the principle in his book “Natural Magic”. Johannes Kepler mentions Camera Obscura in 1604.
Camera = chambre (room), Obscura = dark (or cover).
| |
|
|
| |
Why is it called a "camera"..?
The word Camera is today's short name for Camera Obscura (which originally means “a dark room”).
Origin of the word Obscura means "dark" or "covered", and the word Camera means Chambre and was used originally only as a Latin or alien word, actually only for Spanish soldiers' rooms, until popularized in connection with photography in 1727: “Camera Obscura”.
In 1793 the slang term “camera” was used by Sterne Tr. Shandy: “Will make drawings of you in the camera” and by Foster (1878), “The eye is a camera”.

Ibn-al-Haytham mentioned Camera Obscura in his "Book of Optics" in 1021.
The concept of Camera Obscura was described by Iraqi scientist Ibn-al-Haytham in his book, “Book of Optics” (1021) and by Leonardo da Vinci in 1500; popularized and made widely known in 1589 by Baptista Porta when he mentioned the principle in his book “Natural Magic”. Johannes Kepler mentions Camera Obscura in 1604.
Camera = chambre (room), Obscura = dark (or cover). |
|
| |
|
|
Contrast - The degree of difference between tones in a picture. Latin contra- ‘against’ + stare ‘stand.’
 |
|
 |
| Normal to low contrast |
|
High contrast |
| |
|
|
Depth - Distance between front and back. Distance from viewer and object.
| |
 |
| |
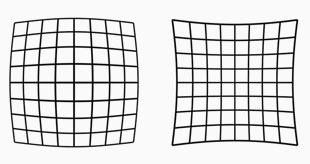
Lens distortion looks like this. The lines are not straight. Our eye uses distortion correction. Lens designers can design lenses so they have very little distortion, or they can make less complicated lens designs and "fix" the distortion in software. |
| |
|
Distortion = In photo optics/lenses: When straight lines in a scene don't remain straight because of optical aberration.
Lens designers can correct for distortion to a degree so the whole image field is perfect corrected and all lines remain straight. In modern lens design many designs rely on Software Distortion Correction (SDC).
The eye adjusts for distortion so we always see vertical and horizontal lines straight when we look at things. Even when you get new prescription glasses (if you use such), you will often experience distortion in your new glasses. After a few days they eyes have adjusted for the glasses and the distortion you saw to begin with is now gone. Software Distortion Correction (SDC) is far behind what the human eye can perform of adjustments. (Also see my definition on Perspective for more on the eye and optics)
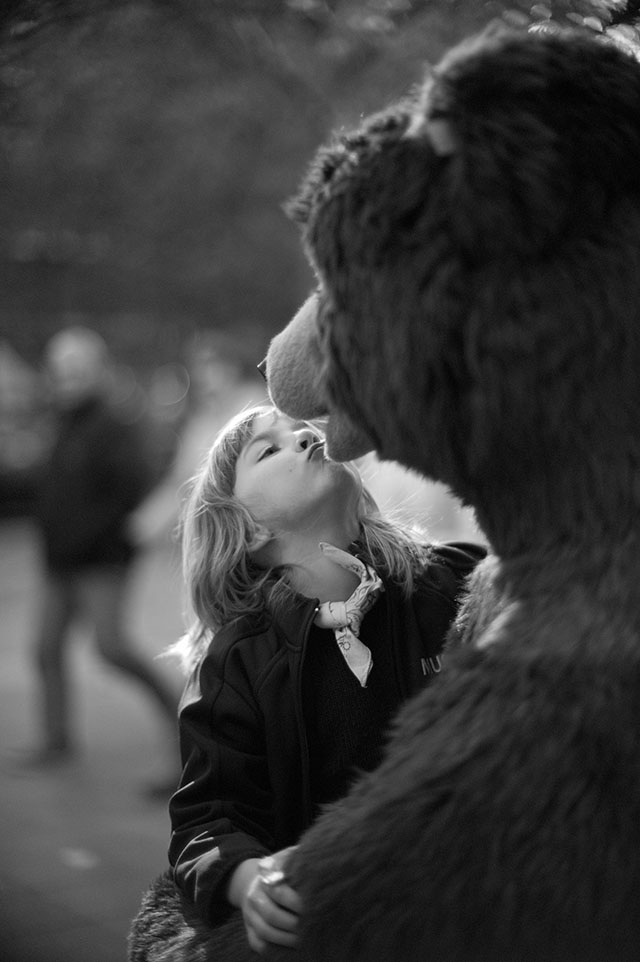

Narrow Dept Of Field in use: The face is in focus, the hand in front is slightly out of focus, the background is much out of focus and blurry, reduced to an atmosphere. Leica 50mm Noctilux f/1.0 at f/1.0 and 2.5 meters distance to subject in focus. © Thorsten Overgaard.
 |
|
 |
| 50mm f/1.4 lens at f/1.4. |
|
50mm f/1.4 lens at f/5.6 |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
| |
The lines on this 28mm lens indicates the DOF. Here the focus is on infinity, and if the lens is stopped down to f/1.6, objects from 1.8 meter to ininity will be 'acceptable sharp'. |
| |
|
DOF = Depth of Field (or Depth of Focus), an expression for how deep the focus is, or (more often use to express) how narrow the area of focus is. This is how much of the image, measured in depth or ditance, will be in focus or "acceptable sharp".
The appearance of the DOF is determined by:
1) aperture (the smaller the aperture hole is, the deeper is the depth of field, and opposite, the wider open a lens you se, the more narrow will the DOF be) and
2) distance to the subject (the farther away, the larger area is sharp; the closer the subject in focus is, the more narrow the DOF gets)..
The DOF scale measurement on top of the Leica lenses shows lines for each f-stop that indicates from which distance to which distance the image will be sharp. Shallow DOF is a generally used term in photography that refer to lenses with very narrow focus tolerance, like f/1.4 and f/0.95 lenses, which can be used to do selective focus; making irrelevant subjects in the foreground and background blurry so only the subjects of essence are in focus and catches the viewers eye).
in modern cameras like the Leica SL2, the camera has a DOF scale inside the viewfinder. As DOF is the same for all lens brands and designs, only depending on focal length, distance and aperture f-stop, the camera can calculate it and show a 'digital DOF scale" in the viewfinder.
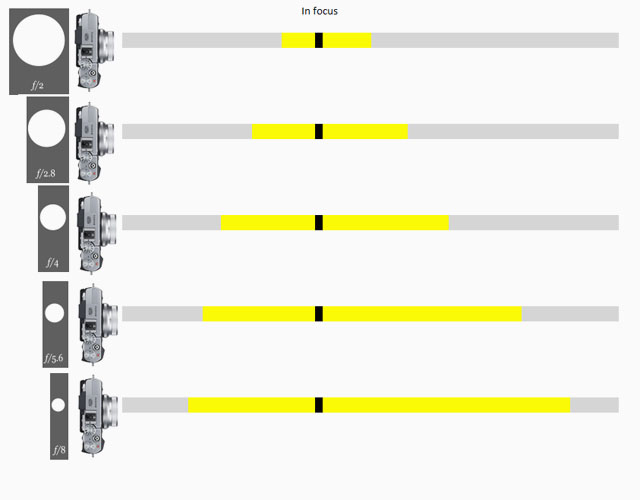
Depth Of Field scale from Fujifilm, same lens with different aperture settings from f/2.0 to f/8.0.
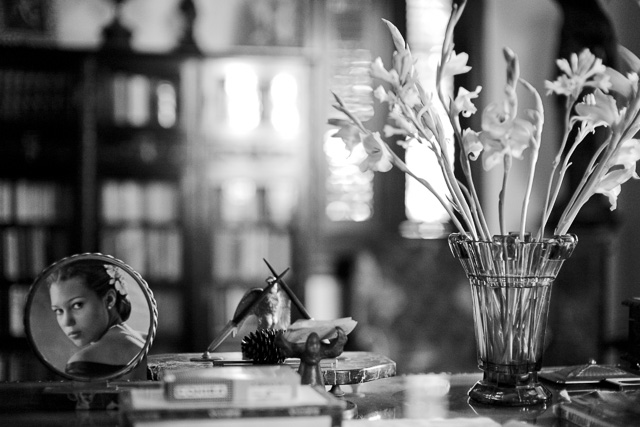

Depth of Field: Focus is on the flowers and the photograph on the desk and the foreground and background is blurred as the depth of field is narrow. If one stop down the aperture of the lens from f/1.4 to f/5.6, more will be in focus. If one stop down the lens to f/16 even more (if not all) will be in forcus. Another rule: The closer you go to a subject (the less focusing range), the more narrow the Depth of Field will be. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Depth - Distance between front and back. Distance from viewer and object.
Elmarit = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f2.8 . The name is obviously derived from the earlier (and slower) "Elmar" designation. Not every f/2.8 lens is called an "Elmarit" though, the most obvious current exception being the 50mm f2.8 Elmar-M collapsible lens which for nostalgia and marketing reasons has kept the original 1930's Elmar name (the 50mm f3.5 collapsible Elmar, manufactured 1930-59, was one of Leica's most famous and popular lenses).
f/ (f-stop, also known as aperture).
f- (focal length). Often given in mm, for example 90mm. In the past they were often given in cm or inch, for example 9.5 cm or 3.2 inch.
f/1.25 is the size of the "hole through" the lens, the aperture. f/1.25 means focal length divided with 1.25. In the Leica 75mm NoctiluxM ASPH f/1.25, the "hole through" the lens at f/1.25 is 60mm in diameter. At f/1.4 the "the hole through" is 53.5mm in diameter. At f/4 the "hole through" is 18.75mm in diameter.
Each step smaller from f/1.4 to f/2.0 to f/2.8 to f/4.0 and son on is a reduction ofthe light to half for each step. The Noctilux f/1.25 therefore lets 50% more light in through the lens than a 75/1.4 Summilux.
f-stop = the ratio of the focal length (for example 50mm) of a camera lens to the diameter of the aperture being used for a particular shot. (E.g., f/8, indicating that the focal length is eight times the diameter of the aperture hole: 50mm/8 = 6,25 mm); or the other way around, the hole is the focal length divided with 8).
ORIGIN early 20th cent.: from f (denoting the focal length) and number.
One f-stop is a doubling or halving of the light going through the lens to the film, by adjusting the aperture riing. Adjusting the f-setting from f 1.4 to f.2.0 is halving the light that goes through the lens. Most Leica lenses has half f-stops to enable the photographer to adjust the light more precicely.
Flare = Burst of light. Internal reflections between (and within) lens elements inside a lens. Mostly, flare has a characteristic "space travel" look to it, making it cool. Particularly in older lenses with less or no coating of the glass surfaces to suppress this, it can be a really cool effect. In newer lens designs, the coatings and overall design try to suppress flare and any reflections to a degree, so that there is seldom any flare to be picked up (moving the lens to pick up a strong sunbeam), but instead a "milking out" (or "ghosting") of a circular area of the frame; meaning simply overexposed without any flare-looking flares.
 |
|
 |
Sunlight creating (fairly supressed) flare in the bottom right quadrant of the image of a modern lens. |
|
The camera moved slightly to avoid the flare. |
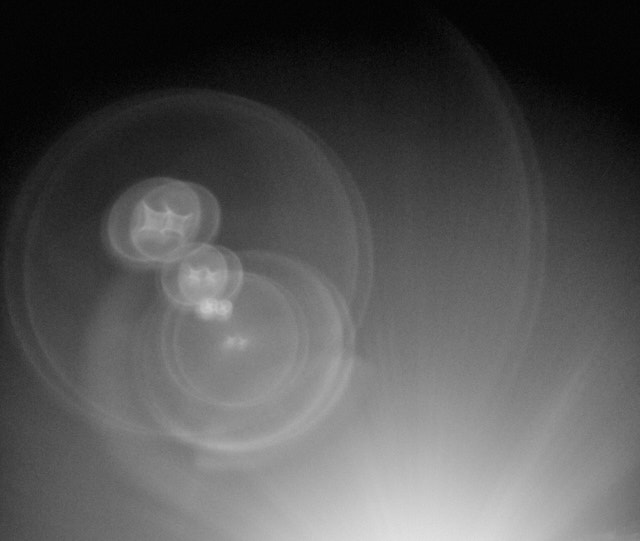

Older lenses with less coating, or without coating, are known to create flare that can look like this (Leica 50mm Summicron-M f/2.0 II Rigid model from the 1960's). © Thorsten Overgaard.

Lens flare in the movie, The Graduate (1967).

Lens flare in Mission Impossible Fallout (2019)

Lens Flare in Star Trek (2013). JJ Abrams famously said, "I know there's too much lens flare ... I just love it so much. But I think admitting you're an addict is the first step towards recovery (ha ha)"
|
| |
 |
| |
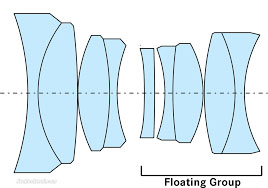
Floating elements (a group of lenses or can also be s aingle lens element). . |
Floating Elements (FLE) = Near focus correction in a lens by having a single lens or a group of lenses floating independently of the other lenses. Most lenses are born with poor performance at their closest focusing distance. Center sharpness may be good, but aberrations and corner softness increase when you’re shooting closeups. Floating elements are lens elements outside of the primary focus group that change position when the lens is focused on a close object, correcting aberrations and improving close up performance.
Floating Elements originally was coined by Canon in the 1960's and quickly became the general term for this feature. Other brands came up with new names for the same thing, Minolta called it Floating Focusing, Nikon used the term Close-Range Correction (CRC), Leica call it FLE/Floating Elements.
Floating elements are for close-focus improvement of image quality and not for reducing "focus shift". Floating elements by themselves cannot reduce focus shift, but by reducing the impact of focus distance on performance, they give the designers more freedom in other areas - which could include minimising focus shift.
(As a side-note, when a lens "rattler when moved, it is not the floating elements "floating around" but can be the IS (Image Stabilization) elements for elense that has that, AF elements for auto focus lenses, or the aperture cage that rattles (as in the case of the Leica 35mm Summilux-M f/1.4 FLE - if you stop down the Summilux to f/16, the sound is usually not there).
| |
 |
| |
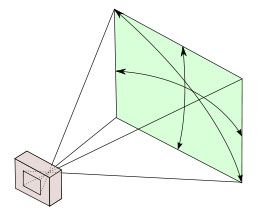
A 28 mm lens has a 74° viewing angle |
| |
|
Focal length = Originally focal length referred to the distance from the sensor (or film in older days) to the center of focus inside the lens (28mm, 50mm, 400mm, etc). Today one call it effective focal length (EFL) as a 400mm lens is not nessesarily 400mm long due to optical constructions that can make it shorter. The 35-420mm zoom on the Leica V-Lux 1 is for example only ca. 135 mm long. Nobody uses that measurement, except those who construct lenses! For users of lenses, focal length refers to how wide the lens sees. The viewing angle, which is often given in for example 90° viewing angle for a 21mm lens, 74° viewing angle for a 28mm lens, 6° viewing angle for a 400mm lens, etc.
Each human eye individually has anywhere from a 120° to 200° angle of view, but focus only in the center.
Focus, in - Sharp and clear in appearance. Focus - “The burning point (of a lens or mirror)”. In Latin the word focus meant fireplace or hearth. The word was probably first employed outside of its Latin literal use as “the burning point of a lens or mirror” in optics, and then came to mean any central point. The German astronomer Johannes Kepler first recorded the word in this sense in 1604.
Focus shift = That the focus of a lens shifts as the aperture changes. For example, if one focus a 50mm lens at f/2.0 and then stop the aperture down to f/8, the focus may change, especially noticeable in close focusing. Modern lenses with floating elements (FLE) where the floating elements adjust for image quality in close-focusing may also help avoid focus shift.
Ghosting = Secondary light or image from internal reflections between (and within) lens elements inside a lens. The reflected light may not always be in focus, so overall it looks like a "milked out" image. A subject in focus has brightened patches in front of it that come from reflections inside the lens. the most elementary look of ghosting is when you look in a rear-view mirror in a car at night and you see doubles of the headlights behind you (a strong one and a weaker one), because the headlights are reflected in a layer of clear glass on top of the mirror glass.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| Degrees of ghosting from strong sunlight entering from outside the frame. To the right the outside light has been shielded with a shade. |
Leica = A compound word derived from " (Lei)tz" and "(ca)mera". Apparently they were originally going to use "LECA", but another camera company already used a similar name in France, so they inserted the 'i' to prevent any confusion.

The word lens derives from lentil, because of the similar shape.
Lens - A piece of glass or similarly transparent material (like water or plastic). It has a shape so that it can direct light rays. The word “Lens” is used both for single piece of glass as well as a camera lens with several lenses that works together. The word lens if often used to refer to the entire camea lens, which is usually compose of seberal lens elements. From ‘lentil’ because similar in shape.
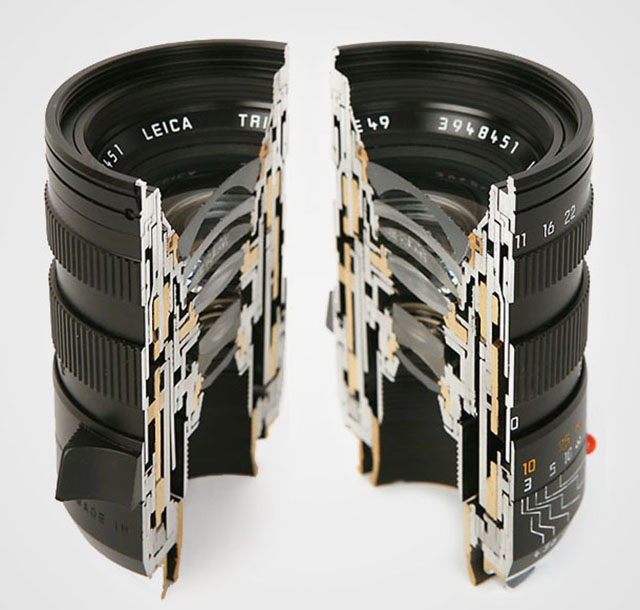

A camera lens consists of several shaped lens elements of glass. The lenses can also be made of simple cheap plastic as in "kit lenses" (sold with a camera as a kit to make a workable cheap package), but it is mostly very exotic glass (that can be heavy or light in weight, very hard or very soft in surface (esay to scratch or very resistant) with each optical glass recipe made to develop very specific qualities in how the glass and final lens treats light. As a general rule, high quality glass is soft, which is why some lenses has as their front and back element, a non-optical lens element that is there to protect the actual optical glass from scratches. As a side noite, Leica made their own glass laboraty, The Leitz Glass Laboratory, from 1949-1989, which deveopled 35 new glass types and took out more than 2,000 patents of glass recipes from more than 50,000 experimental melts of glass. These designs, or recipes, are still used today by the lens designers to obtain very specific optical results. Other lens manufacturers in the world of course have had their glass laboratories, and today one will find an interchange of glass patents amongst production facilities that service Leica, Nikon,, Fuji and so on with optical lens elements.
Lens hood = (also called a Lens shade or Ventilated Shade). A tube or ring attached to the front of a camera lens to prevent unwanted light from reaching the lens and sensor. In the past where lenses were not coated to prevent internal reflections inside the lens, the lens hood was often essential. These days where lenses are coated, the shade serves just as much as decoration and protection (bumper) as well.
ORIGIN Old English hod; related to Dutch hoed, German Hut 'hat,' also to hat.

Lens hood or Lens shade or ventilated shade. In the picture is a ventilated shade with clip-on mount to a 50mm f/2.0 lens. Ventilated means it has openings that allow for view from the viewfinder.
Lens names of Leica distinguish which widest aperture the lens has:
| Noctilux |
f/0.95 - f/1.25 |
| Nocticron |
f/ 1.2 (Leica-designed Panasonic lens) |
| Summilux |
f/ 1.4 - f/1.7 |
| Summicron |
f/2.0 |
| Summarit |
f/2.4 - 2.5 |
| Hektor |
f/1.9 - f/6.3 (used 1930-1960 for screw mount lenses only) |
| Elmarit |
f/2.8 |
| Elmar |
f/2.8 - f/4.5 |
| Elmax |
f/3.5 (only used 1921-1925 for the 50mm Elmax f/3.5) |
| Telyt |
f/2.8 - f/6.8 (used for tele lenses) |
Light = Tiny particles called photons that behaves like both waves and particles. Light makes objects visible by reflecting off of them, and in photography that reflecting off of subjects is what creates textures, shapes, colors and luminance. Light in its natural form (emanating from the sun) also gives life to plants and living things, and makes (most) people happier. So far, nobody has been able to determine exactly what light is. The word photography means “writing with light” (photo = light, -graphy = writing). Read more about light in my book Finding the Magic of Light.
M (as in "M3", "M6", "M7" etc.)
A) The M originally stands for "Messsucher", which is German "Meßsucher" for "Rangefinder". The "3" in M3 was chosen because of the three bright line finders for the 50, 90 and 135 mm lenses. Later the numbers of the M cameras were more or less chosen to follow each other.
M-body evolution in chronologic order:
M3 - MP - M2 - M1 - MD - MDA - M4 - M5 - CL - MD-2 - M4-2 - M4-P - M6 - M6 TTL - M7 - MP - M8 - M8.2 - M9 - M9-P - MM (black and white sensor) - ME (Type 220) - Leica M (Type 240) - Leica M-P 240 - Leica M 246 Monochrom - Leica M-A (type 127, film camera) - Leica M 262 - Leica M-D 262 (without a screen) - Leica M10 - Leica M10-P, Leica M10 Monochrom, Leica M10-R.
B) M also refer to M-mount as the M bayonet that couple the Leica M lenses to the Leica M camera. Before the M bayonet the coupling between the camera and lens was screwmount.
C)
M nowadays refer to the Leica M line of cameras rather than the "Messsucher".

The Leica M bayonet on the Leica M10.
M-mount: The Leica M-mount is a bayonet that was introduced with the Leica M3 camera in 1954 and has been used on all subsequent Leica M cameras, as well as on the Epson R-D1, Konica Hexar RF, Minolta CLE, Ricoh GXR, Rollei 35RF, Voigtländer Bessa, and Zeiss Ikon cameras (2019).
Compared to the previous screw mount (M39), the M
mount requires a quick turn of the lens, and ithe lens is mounted. The patent for the M-bayonet ("Bajonettvorrichtung für die lösbare Verbindung zweier Kamerateile") was registered by Ernst Leitz GmbH 10 February 1950 (patent number DE853384). Hugo Wehrenfennig was credited with the invention.
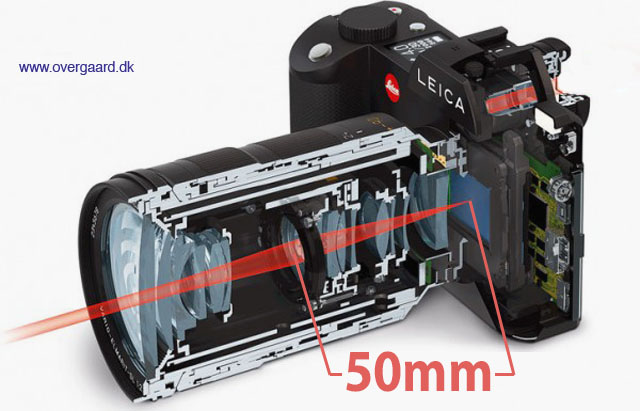

Focal length is determined by the distance from focus inside the lens to sensor surface to, and is given in milliemeters (mm). © Thorsten Overgaard.
mm = millimeter(s), as in a 50mm lens. (Earlier in lens history lenses focal length was given in cm = centimeters; as in a 5 cm lens). For anyone used to centimeters and millimeters, it’s no wonder. But if you grew up with inches, feet and yards, you may have had a hard time grasping what a 50mm lens was. But as lenses were designed first in Europe, the metric system with centimeters and millimeters was used to describe lenses.
(Leica and others made lenses for a while with either meter scale or feet scale; but then eventually started including meter and feet on all the lenses (two scales, usually distinguished with different colors). However, the lens' focal length remained always 50mm, 75mm and so on).
The reason a 50mm lens is a 50mm lens is that there is 50mm from the focus plane (the film or sensor surface) to the center of focus inside the lens. When photography was a young subject, it was engineers who made it all, and the users were expected to understand. The engineers were so into the making of the lenses, that it apparently never dawned upon them that today’s users would think of a 21mm lens as a wide angle lens rather than a lens where there is 21mm from the sensor to the center of focus inside the optics.
ND
Neutral Density filters are grey filters function as 'sunglasses' for lenses. They simply block the light so that a lens can work at for example f/0.95 or f/2.0 in sunshine.
If a camera is set to 200 ISO and the maximum shutter speed is 1/4.000, this will usually result that the lens has to be at f/2.8 or smaller aperture in sunshine. Else the image will over-exposed. So in order til stay within the maximum shutter speed of 1/4.000 and still use a lightstrong lens wide open, one mount a ND-filter that reduce the light with 3 stops (8X) or 6 stops (64x).
For video ND-filters are used quite a lot (as the shutter speed for video is 1/60), and ND-filters are also used to reduce the light for really long multi-exposures at night (stop-motion video and stills).
ND-filters also exist as variable ND-filters so one can adjust the amount of light going through from for example 1 stop (2X) to 6 stops (64X).
ND-filters also exist as graduated ND-filters where the top of the filter is dark and then gradually tone over in no filter (so as to reduce the skylight in a landscape for example).
The ND filters are called Neutral because it is a neutral filter. It doesn't change colors, only the amount of light.
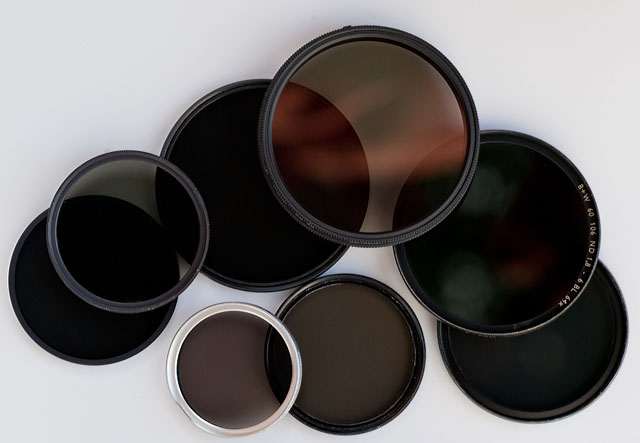

ND-filters / gray-filters.
Optic = Eye or vision. From French optique or medieval Latin opticus, from Greek optikos, from optos ‘seen.’
Perspective = The way objects appear to the eye; their relative position and distance. Also, selective focus (foreground and background out of focus) can change the perception of perspective (also see Three-dimensional). A wide angle "widens" the perspective and makes objects further away appear smaller than they are to the eye; and objects closer, relatively larger than they are to the eye. A tele lens will "flatten" the perspective and often objects further away will appear relatively larger than close objects than they are in real life. A 50mm lens is the one closest to the perspective and enlargement ratio of the human eye.
The word Perspective comes from the latin word for optics (perspicere, per- ‘through’ + specere ‘to look’), and so-called Renaissance painting is simply painting done within the framework of optics and the linear perspective it presents.
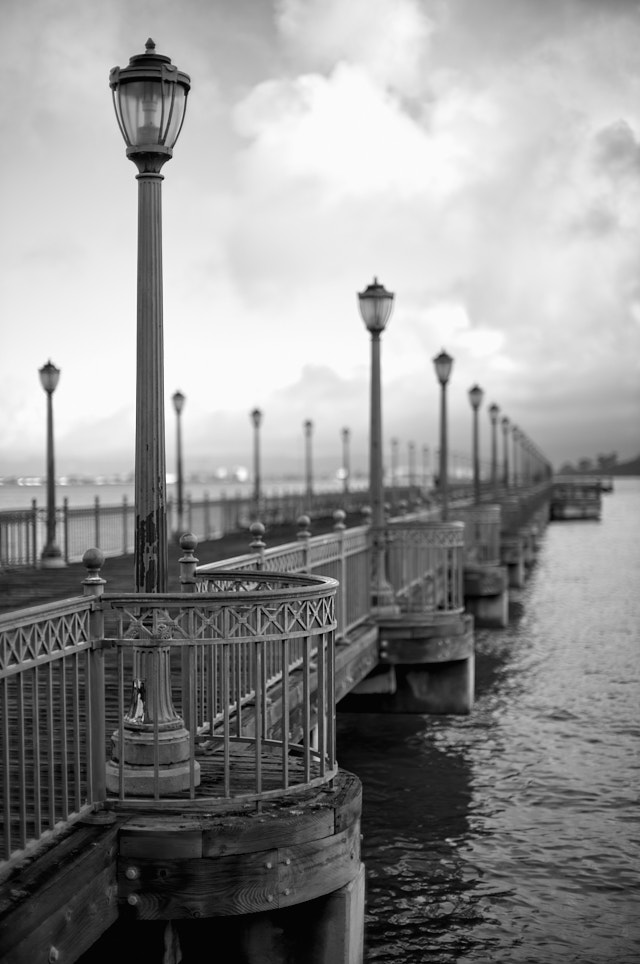

Perspective is relative position and distance. The objects nearby are larger than objects far away. This is how the eye and the mind calculate distance. The eye and the camera automatically captures perspective. In darwing and painting one would see "stupid" two-dimensional drawings 500 years B.C where elements were thrown into the mix without considering that a an object far away must be smaller than if close to the viewer. The word "perspective" comes from "to look through (optics)". Pier 7 in San Francisco by Thorsten Overgaard. Leica M11 with Leica 50mm Noctilux-M ASPH f/0.95.
| |
 |
| |
Vanishing points are the points where lines meet. This is how you make perspective in paintings and drawings (and some times make movie sets or theatre stages appear more three-dimensional than they are) |
| |
|
Painters works with vanishing points, which is where the lines meet, so as to create an illusion of perspective and three-dimensional effect on a two-dimensional painting or drawing.
The human eye corrects for perspective to an extreme degree. We always see vertical lines vertical and horisontal lines horisontal: The eye has a angle of view equivalent to an 8mm wide angle lens, a size ratio equivalent to a 50mm lens and we focus on relatively small area of the viewing field - one at the time. Three things happens that are worth paying attention to:
1) We compile areas of our view that we focus on, to one conceptual image that "we see". Ansel Adams, the great American landscape photographer pointed out that a large camera used for landscape photography capture every detail in focus and sharp so you can view it in detail after; but the eye does not see everything in focus when you try to compose the landscape photography, the eye scans only one part at a time and stitch the idea together. This makes composing or prevision of a landscape photography challenging.
2) We compile areas of our view that we individually adjust the exposure of. A camera adjust the exposure of the whole image frame to one exposure. That's why what looks like a nice picture to the eye of houses in sunshine with a blue sky above, becomes a photograph of darker buildings with a bright white sky: The camera simply can't take one picture that compare to what we "compiled" with our eyes, adjusting for each type of light.
3) Objects (on a table, for example) in the bottom of our viewing field will appear 100% perspective corrected - to a degree that it is impossible to correct in optics, with or without software correction. A wide angle lens, even with little distortion, will exaggerate the proportions of the closet part so it - to the eye - looks wrong.
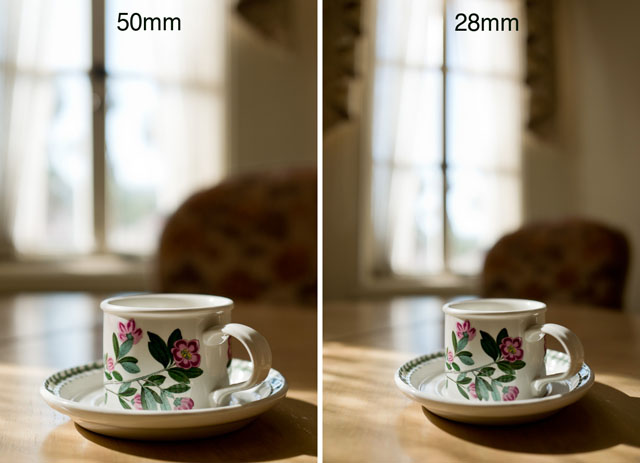

Perspective distortion: Comparing these two photographs you can see how the cup stretches in the 28mm wide angle photograph compared to the 50mm photograph. Both actually has a little stretch because both the cup is in the edge of the frame in both photographs. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Perspective correction - In software like Adobe Lightroom and Capture One Pro there is often a feature to correct perspective (and distortion) like seen below. You can change perspective this way, or at least make believe: If you correct a tall building on teh vertical lines, you will notice that the height of the windows doesn't match the perspective. If the building is with straight lines, the windows should all be of the same size. But a tall building seen from below and corrected with software will have taller windows (closer to camera) in the bottom than in the top (further away from the camera originally).
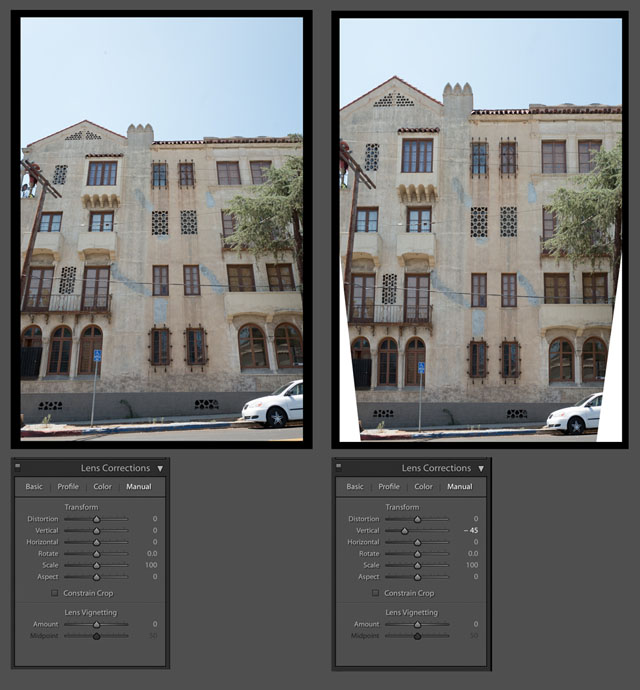
Perspective correction in Adobe Lightroom. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
Saturation: How colorful, intense or pure the color is. Less saturation would be less colorful, more saturation would be more colorful. In today’s photography, de-saturating a photo on the computer will gradually make it less and less colorful; and full de-saturation would make it into a black and white photo.

A photo from Verona, Italy de-saturated, normal saturated and over-saturated. © Thorsten Overgaard.
Sharpness - See “Focus”
| |
 |
| |
The 6-bit code on the flange of the lens is read by the sensor on the Leica M bayonet of all digital Leica M cameras since 2006. © Thorsten Overgaard. |
| |
|
Six-bit code (6-bit code) - An engraving on the flange of M-lenses that makes it possible for digital M-cameras to recognize the lens that has been mounted. The camera can include information on the attached lens and its focal length in EXIF data and make digital corrections for lens-specific flaws, such as color-cast or vignetting. Six-bit coding was introduced for all M-lenses sold since 2006, but many older lenses can be retrofitted with the code at Leica Camera AG in Wetzlar.
Summilux = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f1.4 , "-lux" added for "light" (ie. the enhanced light gathering abilities). In Leica terminology a Summilux is always a f/1.4 lens and a Summicron is a f/2.0 lens.
Summicron = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f/2.0 . There are many guesses how this name came about, a popular one being that the "summi" came from "summit" (summit means the highest point of a hill or mountain; the highest attainable level of achievement) while the "cron" came from "chroma" (ie. for colour). Not so: The name (Summi)cron was used because the lens used Crown glass for the first time, which Leitz bought from Chance Brothers in England. The first batch of lenses were named Summikron (Crown = Krone in Deutsch). The Summi(cron) is a development from the orignal Summar (the 50mm f2.0 lens anno 1933). Vario-Summicron, Vario-Elmarit is Leica Camera AG's name for zoom lenses, for example the Vario-Summicron f/2.0 as the one that is on the Leica Digilux 2.
Summilux = Refers to the maximum lens aperture - here f/1.4 , "-lux" added for "light" (ie. the enhanced light gathering abilities). In Leica terminology a Summilux is always a f/1.4 lens and a Summicron is a f/2.0 lens.
Three-dimensional = Having the three dimensions of height, width and depth. In photography and lens design, three-dimensional effect is also the perception of even small micro-details; the texture of skin can appear flat and dead or three-dimensional and alive. Also, selective focus (foreground and background out of focus) can change the perception of depth. Also see Perspective.
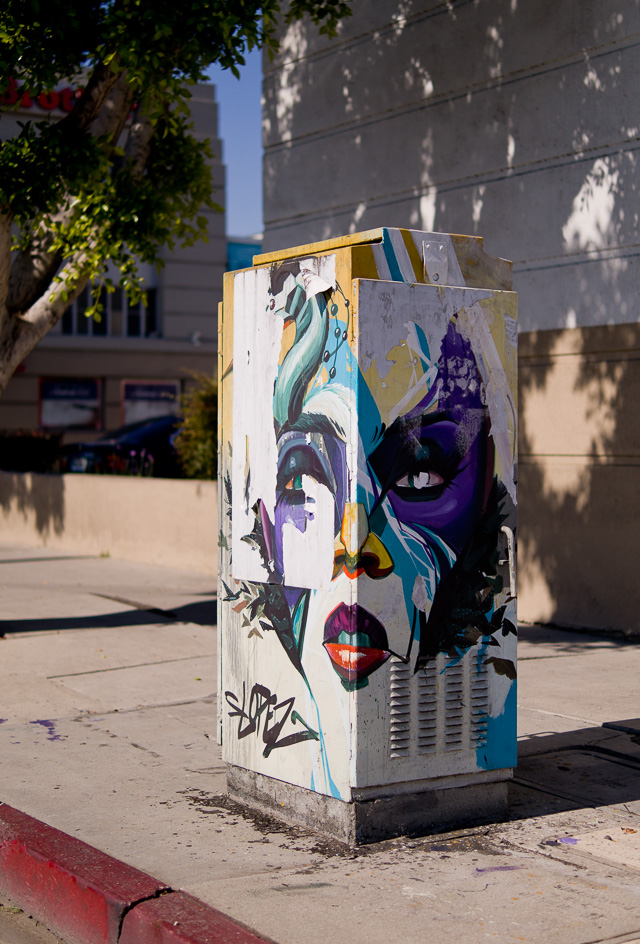

Three-dimensional = Having the three dimensions of height, width and depth. Melrose Avenue in Los Angeles. Leica TL2 with Leica 35mm Summilux-TL ASPH f/1.4. © 2017 Thorsten Overgaard.
Ventilated Shade - A shade is a hood in front of a lens that provides shade from light going straight onto the lens from outside what you are photographing, which could cause internal reflections like flare, which would make the picture less contrasty.
The ventilated shade has holes so it doesn't obstructs the view from the viewfinder. In many of today’s mirrorless cameras where there is no viewfinder looking ver the lens, so there is no actual need for a ventilated shade; but they are considered classic or vintage looking and are still in high demand. It makes no difference for the purpose of the shade (to create shadow) if it is ventilated or not.
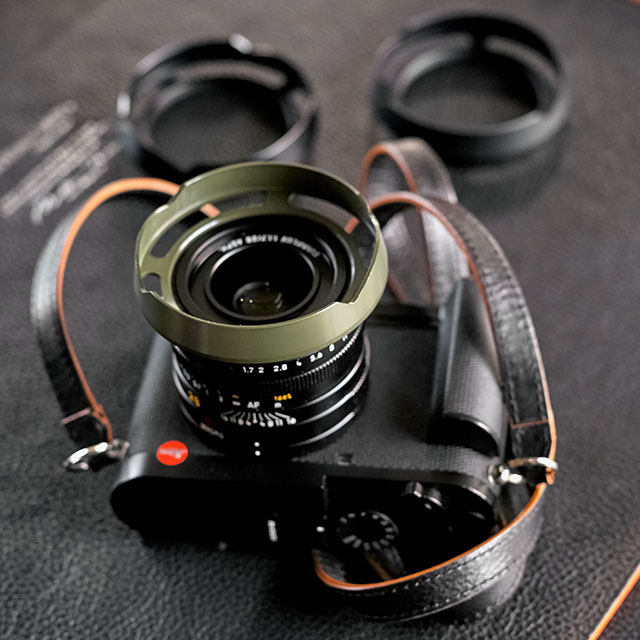

Ventilated Shade for the Leica Q. I make ventilated shades for most lenses and sell them from here.
|
![]()
