By: Thorsten Overgaard. December 24, 2016.
Add to Flipboard Magazine.
In May 1934, the then 32-year old Ansel Adams wrote a famous essay in "Modern Photography", a magazine that then had a readership of 400,000 readers.
The essay is written at a time where photography was young and wasn't established as an art. It was still an ongoing discussion what photography actually was. I felt it was worth making this historic article available again.
Ansel Adams was later criticizeed for his less-than-precise version of the history of photography, but overall he received high praise for the essay that crowns the ultimate achievement of photography (in his estimation) as "straight photography". It is also the first published definition of visualization from Ansel Adams.
This is a complete reprint of the Ansel Adams essay, with the three of the four photos that also appeared elsewhere in this issue of "Modern Photography - 1934-1935 - The Studio Annual of Camera Art."
Enjoy!
Some confusion still exists as to what photography is aiming at. Mr. Ansel Adams here traces the underlying principles which should govern the photograph.
By: Ansel Adams, San Francisco, April 1934. (Reprint December 24, 2016).
CRITICISM and discussion of Modern Art frequently admit an unfortunate error: the failure of properly defining the terms "new" and "modern."
These terms have but slight actual meaning in themselves – they are fluent and convenient expressions that do not stand as final definitions of contemporary work. Art is in a constant state of change, reacting always to the intellectual and aesthetic trends of Society. At this time the Arts, and especially Photography, require not so much to be labelled as to be understood. The full understanding of a medium of art is evolved only by analysis of its inherent qualities, its development, and its functional direction, and not through established precedents of opinion and ambiguous terminology.
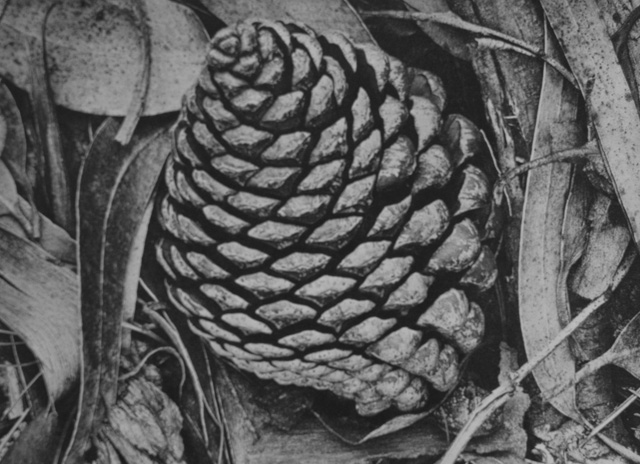

Ansel Adams: Pine Comes and Eucalyptus Leaves. "True photogprahic quality, every shape delicately distinct." 4x5 Corona view camera, Goerz Dagor 12-in. lens, 1 second, f/4.5, Eastman super-sensitive panchromatic film.
The entire perspective of Photography, from the time of the Camera Obscura to the present day, reveals four clearly defined periods of development: the Experimental, the Factual, the Pictorial, and the Photographic Renaissance. As we are not discussing the history of Photography in this article, it will suffice that we generalize the progress of the medium largely from the aesthetic point of view, and relate our generalizations to the contemporary definition of Photography as a fine art.
1. The Experimental Period
This period includes the invention and application of the Camera Obscura, and the optical and chemical experiments prior to the production of the first permanent photographic print (circa 1825). The Experimental Period relates directly to art only through the use of the Camera Obscura, which indicated to painters that the representation of actuality could be effected by "light-and-shade" (do not confound this with the Impressionism of later times).
As Wilenski says (in his book "The Modern Movement in Art", this approach was contrary to the theories of formal ("architectural") art; he illustrates his point with detailed comparison of the paintings of Corot and others, with photo graphs of similar subject material. Possibly the influence of the Camera Obscura and the early photography was not always as obvious as Wilenski suggests, but that it was profound there can be little doubt.
2. The Factual Period
This period relates to Photography from the achievement of the first permanent photographic print to the inception of the Pictorial Period (circa 1890-1900). About 1825 a new element amplified the influence of the optical image on art; the image of the Camera Obscura became a picture. It was proven possible to produce a lasting picture through the agencies of light and chemical compounds, and with relatively simple processes unlimited numbers of such pictures might be produced at will. Here, indeed, was a challenge to painters, etchers, and draughtsmen; the new medium rendered accuracy of line and texture with a perfection the human hand could not attain and no other medium could convey. The artists, while outwardly critical of Photography as hard, mechanical, and negative to the true expression of the "Human Soul," adopted many of its properties. The influence of Photography on the art of the past century is difficult to estimate.
The first photography was completely objective. Even the magnificent work of David Octavius Hill was motivated by the necessity of securing efficient sketches for the many likenesses in his ambitious canvas portraying the First General Assembly of the Scottish Free Church. Photography, in Hill's estimation, was a means to an end-a method of expediting a "work of art." The essential beauty of his work lies precisely in its clean objectivity he anticipated the fundamental aesthetic premise of the medium without, we are quite certain, being aware of the value of his contribution.
For many decades thereafter, through the wide application of the Daguerreotype and the development of the "wet” plate, Photography was satisfied to record actuality-to be literally representative. It is undoubtedly true that this sustained objectivity served to establish the medium on a solid and impregnable foundation ; had Photography become at once self-consciously artistic its subsequent development would be difficult to imagine.

Ansel Adams: Nevada Fall, Yousemite Valle, California. "A superb study of water, considered by the photographer his best landscape photograph." 8x10 Folmer Universal camera, Goerz Dagor 12-in. lens, with K1 filter, 1/75 second; f/16, Eastman super-sensitive panchromatic film.
3. The Pictorial Period
This, the third stage of Photography, was in full control towards the close of the nineteenth century. The photography of this period reflects many variants of the romantic tendencies and the vague, shallow, and unforgivably sentimental conceptions of the "Mauve" years.
Pictorialism represents the capitulation of the photographers to the mode and opinion of those times; an impressive number of processes were developed to turn the camera-image into something else (the transition was effected with astonishing popular success). What vast energy and inventiveness was applied to the solution of a basically false hypothesis! Photography literally covered the earth, but the integrity of the medium was in a pitiful condition. Pictorialism discards the pure photographic technique and view-point in favor of superficial imitation of other graphic mediums. While a shallow imitation of the other art-forms was often obtained, their aesthetic substance was never achieved by the Camera, and Photography was thereupon vulnerable, and properly so, to depreciatory criticism and the frank denial of a position among the fine arts. This does not imply any conscious insincerity to the motives of the Pictorialists-it merely indicates that they failed to apply the logic and aesthetic principles of the medium to their production. It was undeniably difficult to justify a logical and objective point of view in the face of world-wide sentimentalism and subjective indulgences. In addition, the formation of academic Societies, Clubs, and Saloons firmly cemented Pictorial tendencies to the solemn walls of Convention and Precedent. The precedent of the Pictorialists eliminates the achievement of the Factual Period and reverts to late Renaissance ideals. Fortunately, during the first part of the Pictorial Period there were a few insurgents who were dissatisfied with the accepted conceptions of the medium, and who suspected the vast potentials of Photography as a true art-form.
Gradually drawing apart from the popular trend, they experimented in the fields of straight photography and adapted the awakening thought of advanced artists and intellectuals to their aesthetic inclinations. The leader of this group was unquestionably Alfred Stieglitz, who is still one of the great forces in the world of art.
Stieglitz has always anticipated the progress of Photography; considering the medium equal to the other arts, he has adequately supported his belief through his own magnificent work and the encouragement of his protégés. Hill and Stieglitz are the two immortals of Photography-the Pioneer and the Emancipator of the new art.
4. The Photographic Renaissance
The beginnings of this period are uncertain unless we consider as such the first work of a few individuals around 1895-1900. As a movement, it is scarcely fifteen or twenty years of age. The tremendous impact of Stieglitz' work on the photographic world effected a profound reaction – Photography began to be thought of as an art. Stirred by the intense devotion of a few leaders to the true values of the medium, a group has evolved which is dedicated to the simpler and more direct aspects of the art. Liberated by the important improvements in apparatus and materials of the last few years the photographer finds himself in a most advantageous position; public appreciation and understanding is increasing by leaps and bounds, fields of application are widening, museums and galleries are exhibiting photography, and collections are being formed. The Pictorialist is still with us; his imitative faculty is revealed in that he often attempts to restate the "new" Photography in terms of antiquated technique. We may be certain that the Photographic Renaissance is well on its way, but there remains much chaff to clean from the essential grain. Before we attempt a more precise analysis of pure photography, we should inquire as to what this cursory sketch of the four periods of Photography indicates. We may all agree that the medium was essentially defined in the first permanent print. All the elements of Photography were expressed in that first print: the lens, the negative, the positive, chemicals and their reaction to light. Crude indeed, but few beginnings are less crude than the first successful photography. As the medium developed the elements were refined, mutually adjusted, and standardized. In the first stages of the art people were too occupied making photographs to think much, or at all, about aesthetic significance. Let us refer to one outstanding American photographer of early days: Matthew Brady, who made great numbers of magnificent photographs of the Civil War.
Immersed in the trying times of the 1860's, Brady reacted to the great upheaval with the desire to participate in the application of his art. He made the best photographs he could, honestly, directly, without motives other than to record the details of that somber pageant. The results are moving, sincere, and of immense historic value. Their emotional quality lies, not in the implications of specific scenes, nor in our sentimental musings on the past, but in the absolute sincerity of expression in relation to the medium employed. A conscious attempt to convey the emotional aspects of the Civil War could not attain what the objective realism of Brady's work implies. Later, in France, Atget puttered about Paris with his camera, making precious records of his city and his time. Again we find the direct and honest attitude towards the medium. Atget lived in the dry-plate era, and his photographs are as mechanically superior to Brady's as Brady's are to Hill's. But mere mechanical superiority does not mean very much; technique-the use of mechanics-was lifted in the production of all three photographers to almost equal heights. Stieglitz, Strand, and Weston carry on this devotion to the medium, and it is on this foundation that Photography will endure. Photography was first a means of representation, illustration, and the communication of visual fact; its direct aesthetic significance and capacities were revealed later. Architecture, Decoration, and Language have followed a similar curve of transition from a purely functional literalism to an intellectual aesthetic expressionism. But it is not enough to cite the accomplishment of the past and the strivings of the present to establish an adequate rationale of the medium of Photography. We must integrate the medium into its elements and each element must be defined and related to the aspect of the whole. Let us briefly discuss the various elements in sequence:
I. The Photographic Point of View
The camera makes an image-record of the object before it. It records the subject in terms of the optical properties of the lens, and the chemical and physical properties of the negative and print. The control of that record lies in the selection by the photographer and in his understanding of the photographic processes at his command. The photographer visualizes his conception of the subject as presented in the final print. He achieves the expression of his visualization through his technique-aesthetic, intellectual, and mechanical. He cannot alter the essential qualities of the subject-he can only select those qualities and the aspect of the subject that relates to his conception, and he can employ logically only pure photo graphic means to gain his objective. The photograph is inescapably a photograph, no matter what manipulation or alteration is imposed on negative or print; the intrusion of any technique which is not purely photographic effects a crude contradiction, and the integrity of the medium is destroyed. A true art medium exists as a thing in itself; powers and limitations must be recognized.
II. The Photographic Composition
The theory of photographic composition has little to do with the theories of composition in other mediums. The painter, for instance, organized his subject to fit preconceived space or formal pattern: the photographer analyses his subject in its "geometric" structure and is obliged to define a space in which the subject will be suitably expressed. Painting is a synthetic process., photography an analytic process; a world of difference lies between them. The geometric elements of photographic composition are influenced by the "weight" or intensity of the tonal masses; the strict linear placement is adjusted thereto. As the photographer is powerless to alter the linear and mass relationships of the subject to any considerable degree, it is evident that photo graphic composition is, at best, a compromise. It is the degree of this compromise which indicated the weakness or the power of the composition. The conscious arrangement of the subject deprives photography of its opportunity to isolate and select compositions from nature. Most advertising and Commercial Photography done today is more the Art of Decoration than the Art of Photography. This problem is quite complex, especially in relation to Montage, and cannot be covered here. Briefly, it involves surface (the aesthetics of two-dimensionalism), tonal contrasts (chiaroscuro), and time (staticism – the perpetuation of the moment). These elements must be understood before the true enjoyment of production or appreciation of a good photographic composition is realized.
III. The Clarity of the Photograph
Strictly speaking, line is not a photographic term; it is edge that takes the place in photography of line in other graphic mediums. The edge must be clear, and the deline ation of the most minute detail must be attained in all sections of the picture. There should be no part of the image "out of-focus”; the lens is not imitating the eye at any one moment of time. The lens is capable of producing image detail on one or many focal-planes (with proper aperture) which is beyond the power of the eye to resolve. This microscopic revelation of the lens is one of the dominant properties of photography, and both the negative and paper on which the print is made should preserve it to the greatest possible degree. Diffusion, and the use of rough papers for prints, serve to reject one of the basic premises of Photography.
ation of the most minute detail must be attained in all sections of the picture. There should be no part of the image "out of-focus”; the lens is not imitating the eye at any one moment of time. The lens is capable of producing image detail on one or many focal-planes (with proper aperture) which is beyond the power of the eye to resolve. This microscopic revelation of the lens is one of the dominant properties of photography, and both the negative and paper on which the print is made should preserve it to the greatest possible degree. Diffusion, and the use of rough papers for prints, serve to reject one of the basic premises of Photography.
IV. The Tonal Values of the Photograph
It is evident that tonal values in Photography have little to do with tonal values in painting, etc. It is not in the imitation of the detail and values of the subject that the intense realism of the photograph lies – it is in the emotional relationship of tone and texture obtained by strictly photographic processes and presented on material which does not destroy the full clarity of the image. Between the extremes of black and white possible in photography, there are myriad subtle intensities of tone-all, when in proper relation to the whole, serving to indicate the play of light upon substance. Every part of a photograph should suggest subject-substance; a solid white or black without structural or tonal suggestion is. not a true photographic tone.
V. Texture in Photography
Texture, in the completed photograph, is the product of detail and depth of tone. The emotional quality of substance and texture requires more than photometric accuracy; it is, to quote Wilenski again, the “enlargement of experience” – the experience of enriched detail, for example, which must be conveyed. Most photography suffers from lack of depth in printing; it is chiefly in the deeper registers of tone that the full beauty of the photograph is revealed.
VI. Colour of Photography
Photography is essentially a black-and-white medium. The intrusion of colour or of dominating tones in the print seriously affects the plane of the monotonal photographic image. The most successful colour-photography is process engraving, which is not photography in the strict meaning of the term.
VII. The Presentation of the Photograph
As simple presentation as possible is required-a plain card with no frills, embossing, lines, etc., is the best possible carrier for a black-and-white print. Water-colours and etchings are usually presented with dignity, and photographs should not suffer in this respect by over-elaborate mounts and folders. A glossy print displayed under glass is the most perfect presentation of the photographic image.
VIII. The Technical Approach to Photography*
Most photography is injured by over-doing the laboratory aspects of the medium than by under-doing them. Let it suffice to state that the simpler and more efficient the technical equipment and procedure the better. Most of the finest contemporary photographers are conspicuous in the simplicity of their apparatus and production technique.
It is evident, on thorough analysis of the past and present aspects of photography that, in many respects, the New Photography is not "new" at all. It is the rediscovery and amplification of the real Factual photography applied to the contemporary artistic and social point of view, and enormously expanded through the technical developments of our time. The New Photography is functional, intellectual, emotional, and social, and may well claim an important position among the Fine Arts. Apart from the attempts of certain photographers to imitate aspects of abstract art, and those who sacrifice dignity for theatrics, there are many individuals throughout the world who evidence a profound respect for the medium and are engaged in serious and important photographic expression. Space forbids adequate mention of all the adherents of pure photography to-day. In America, we are endowed with many of the finest living photographers Stieglitz, Strand, Weston, Sheeler, Evans, and others of great ability.
A phase of contemporary photography which is of great importance is what might well be termed the Photo-document. The Photo-document is nothing more than significant genre, a genre related to the contemporary scene. It represents, in its best form, the logical limits of social propaganda through photography; the human elements dominate, but they dominate through comment rather than direct and intentional propaganda. The rare subtlety and intensity of this comment of the Photo-document is sufficient answer to the criticism that Photography is austere and remote in relation to Human values.
Study the pictures of Hill, Atget, and others of earlier years, then turn to the Photography of the last decade that meets, more or less, the purest definition of the medium. The essential relationship of the two periods cannot be ignored. Photography makes the moment enduring and eloquent.
In seeking a qualifying word to label the production of our time, the term "contemporary" may be advanced, but it is quite unnecessary — the best definition of the camera work of today is just Photography.
We may expect periods of great achievement and periods of decadence, but we are certain that the final test of any art form is its ability to continue as an instrument of human expression through the cycles of human progress.
* Refers to four consecutive articles on technique in "Camera Craft," San Francisco, beginning January, 1934.
ANSEL ADAMS
San Francisco, April, 1934
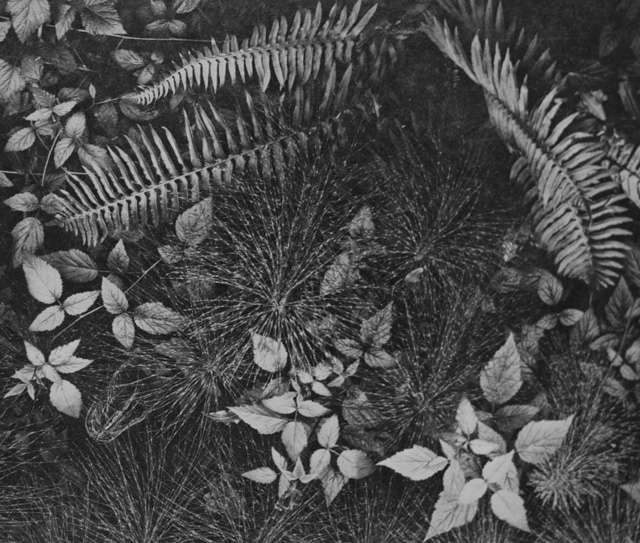

Ansel Adams:
Leaves. "The camera reveals the pattern of nature." 4x5 Corona view camera, Goerz Dagor 4 1/2-in. lens, 1 second, f/4.5, Eastman super-sensitive panchromatic film.
I hope you enjoyed this "The Story Behind That Picture" today. As always, feel free to e-mail me with ideas, suggestions and questions.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Join the New Thorsten Overgaard
Photography Extension Course
"My wife game me this course and I absolutely love it.
Now I think more in light and shadows. Used a lot of the techniques on a recent trip and
my photos have improved a lot. Well done, Thorsten!"
S.N. (Mexico)
"I am happy with my purchase of the extension course. Well written, easy to understand"
K.D. (USA)
“I very much enjoy the incredible knowledge”
V.V. (United Kingdom)
"Addictive, beautifully and simplistically written. Just amazing. Cleared my concepts"
V.P. (USA)
"The extension course is the best course I read about photography (and I'm still at the beginning)"
M.S. (Luxembourg)
"I'm already in page 81 of the Extension Course, and your communication and words provoked a change in me at an aesthetic level that I felt but I couldn't explain"
C.L. (USA)
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
New: The Digital Photographer's Extension Course
Learn the basics of photography with Thorsten Overgaard
I teach you the basics of photography in an easy-to-understand and step-by-step way that anyone from age 12 to 90 years can understand and easily apply. This extension course is for everyone from 12-90 years.
The intention with this extension course is to get you going in your photography adventure with lightning speed and inspire you to reach to new heights.
Enjoy!
Specially tailored for Leica and digital photographers.
The waiting list is over!
After a couple of years with a long waiting list, I have finally redesigned the course so I can handle the students interested in this course. Not only that. The number of pages has gone up from 120 to 340..!
You work at your own pace after you recieve the full package of material via mail. It works as PDF on computer, iPad, Kindle, or - if you like - make your own print.
More info ---> |
|
|
Join the Home School for
Leica and Digital Photographers

Only $998.00


Buy now. Instant delivery by mail.
ITEM #2140-0122 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
![]()
